PCR-RFLP screening of polymorphisms associated with benzimidazole resistance in Necator americanus and Ascaris lumbricoides from different geographical regions in Brazil
- PMID: 30222749
- PMCID: PMC6141064
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0006766
PCR-RFLP screening of polymorphisms associated with benzimidazole resistance in Necator americanus and Ascaris lumbricoides from different geographical regions in Brazil
Abstract
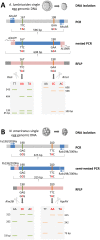
Ascaris lumbricoides and Necator americanus are soil-transmitted parasites with global geographic distribution, and they represent some of the most common and neglected infections in the world. Periodic treatment with mass drug administration (MDA) in endemic areas is the recommended action put forth by the World Health Organization. However, MDA can cause the selection of subpopulations that possess the genetic ability to overcome the mechanism of drug action. In fact, beta-tubulin gene mutations (codons 167, 198 and 200) are correlated with benzimidazole resistance in nematodes of veterinary importance. It is possible that these SNPs also have strong correlation with treatment resistance in the human geohelminths A. lumbricoides, Trichuris trichiura and hookworms. Here, we aimed to investigate the presence of some of these canonical molecular markers associated with parasite resistance to benzimidazole in N. americanus and A. lumbricoides collected from six Brazilian states. Nested-PCR and PCR-RFLP were used to detect mutations at codons 167 and 198 in 601 individual eggs of A. lumbricoides collected from 62 human stool samples; however, no mutations were found. Codons 198 and 200 were tested in 552 N. americanus eggs collected from 48 patients using the same methodology, which presented a relative frequency of 1.4% and 1.1%, respectively. The presence of these SNPs in N. americanus eggs is an important finding, indicating that with high benzimidazole drug pressure there is potential for benzimidazole resistance to be selected in this hookworm. However, at these low frequencies it does not indicate that there is at present any benzimidazole resistance problem. This is the first systematic study performed in South America, and the study yielded a landscape of the genetic variants in the beta-tubulin gene and anthelmintic resistance to soil-transmitted parasites detected by a simple, rapid and affordable genotyping assay of individual eggs.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Improving stool sample processing and pyrosequencing for quantifying benzimidazole resistance alleles in Trichuris trichiura and Necator americanus pooled eggs.Parasit Vectors. 2021 Sep 25;14(1):490. doi: 10.1186/s13071-021-04941-w. Parasit Vectors. 2021. PMID: 34563247 Free PMC article.
-
First identification of the benzimidazole resistance-associated F200Y SNP in the beta-tubulin gene in Ascaris lumbricoides.PLoS One. 2019 Oct 17;14(10):e0224108. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0224108. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 31622428 Free PMC article.
-
Assays to detect beta-tubulin codon 200 polymorphism in Trichuris trichiura and Ascaris lumbricoides.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2009;3(3):e397. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0000397. Epub 2009 Mar 24. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2009. PMID: 19308251 Free PMC article.
-
Benzimidazole Resistance-Associated Mutations in the β-tubulin Gene of Hookworms: A Systematic Review.Parasitol Res. 2024 Dec 9;123(12):405. doi: 10.1007/s00436-024-08432-6. Parasitol Res. 2024. PMID: 39652258
-
Important Nematodes in Children.Pediatr Clin North Am. 2022 Feb;69(1):129-139. doi: 10.1016/j.pcl.2021.08.005. Pediatr Clin North Am. 2022. PMID: 34794670 Review.
Cited by
-
Improving stool sample processing and pyrosequencing for quantifying benzimidazole resistance alleles in Trichuris trichiura and Necator americanus pooled eggs.Parasit Vectors. 2021 Sep 25;14(1):490. doi: 10.1186/s13071-021-04941-w. Parasit Vectors. 2021. PMID: 34563247 Free PMC article.
-
High-Throughput Screening of More Than 30,000 Compounds for Anthelmintics against Gastrointestinal Nematode Parasites.ACS Infect Dis. 2025 Jan 10;11(1):104-120. doi: 10.1021/acsinfecdis.4c00327. Epub 2024 Dec 9. ACS Infect Dis. 2025. PMID: 39653369 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of the β-tubulin gene family in Ascaris lumbricoides and Ascaris suum and its implication for the molecular detection of benzimidazole resistance.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2021 Sep 27;15(9):e0009777. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0009777. eCollection 2021 Sep. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2021. PMID: 34570778 Free PMC article.
-
Worldwide absence of canonical benzimidazole resistance-associated mutations within β-tubulin genes from Ascaris.Parasit Vectors. 2024 May 16;17(1):225. doi: 10.1186/s13071-024-06306-5. Parasit Vectors. 2024. PMID: 38755679 Free PMC article.
-
Single nucleotide polymorphisms associated with benzimidazole resistance of the β-tubulin isotype 1 gene in Ascaris lumbricoides isolated in South Africa.Braz J Infect Dis. 2025 Jun 28;29(5):104556. doi: 10.1016/j.bjid.2025.104556. Online ahead of print. Braz J Infect Dis. 2025. PMID: 40582181 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Humphries D, Mosites E, Otchere J, Twum WA, Woo L, Jones-Sanpei H, et al. Epidemiology of hookworm infection in Kintampo North Municipality, Ghana: patterns of malaria coinfection, anemia, and albendazole treatment failure. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2011;84(5): 792–800. 10.4269/ajtmh.2011.11-0003 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kwa MS, Veenstra JG, Roos MH. Benzimidazole resistance in Haemonchus contortus is correlated with a conserved mutation at amino acid 200 in beta-tubulin isotype 1. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1994;63(2): 299–303. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

