Second language acquisition effects of a primary physical education intervention: A pilot study with young refugees
- PMID: 30222753
- PMCID: PMC6141098
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0203664
Second language acquisition effects of a primary physical education intervention: A pilot study with young refugees
Abstract
Background: A physical education (PE) intervention for young refugees was designed combining physical activity within the context of primary PE games with second language learning activities in German. The intervention was based on theoretical implications from the field of second language acquisition and evidence for positive effects of physical activity on cognitive outcomes (e.g. language acquisition). The aim of this study was to analyze short term effects on second language acquisition.
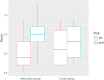
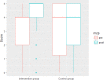
Methods: Sixty-one young refugees were included in the study (age: 8.5 ± 1.4 years). The intervention group participated in language-enriched PE lessons based on an elaborated approach to second language learning acquisition. The control group did not receive any treatment. Both groups were pre-and post-tested in domain specific vocabulary, listening comprehension and use of local prepositions within the context of primary PE games.
Results: Results from linear mixed-effect modelling suggest that the intervention group significantly improved domain specific vocabulary and listening comprehension in comparison to the control group.
Conclusions: The intervention was successful since the PE lessons contributed to the second language acquisition of young refugees. Therefore, this learning approach might also be useful for physical activity based second language learning activities in other PE contexts for early second language learners in primary school.
Conflict of interest statement
The author has declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Native Korean-Speaking Children Learning to Read in English: A Structural Analysis of L2-English Literacy Acquisition.J Psycholinguist Res. 2019 Apr;48(2):391-415. doi: 10.1007/s10936-018-9610-7. J Psycholinguist Res. 2019. PMID: 30370498
-
Facilitating vocabulary acquisition of young English language learners.Lang Speech Hear Serv Sch. 2010 Jul;41(3):314-27. doi: 10.1044/0161-1461(2009/07-0082). Epub 2010 Apr 26. Lang Speech Hear Serv Sch. 2010. PMID: 20421611 Clinical Trial.
-
Cognitive abilities underlying second-language vocabulary acquisition in an early second-language immersion education context: a longitudinal study.J Exp Child Psychol. 2013 Aug;115(4):655-71. doi: 10.1016/j.jecp.2013.04.002. Epub 2013 May 23. J Exp Child Psychol. 2013. PMID: 23708731
-
Effects of Language Skills and Strategy Use on Vocabulary Learning Through Lexical Translation and Inferencing.J Psycholinguist Res. 2020 Dec;49(6):975-991. doi: 10.1007/s10936-020-09720-9. J Psycholinguist Res. 2020. PMID: 32651841 Free PMC article.
-
Learning difficulties or learning English difficulties? Additional language acquisition: an update for paediatricians.J Paediatr Child Health. 2014 Mar;50(3):175-81. doi: 10.1111/jpc.12396. Epub 2013 Oct 18. J Paediatr Child Health. 2014. PMID: 24134139 Review.
Cited by
-
Analyzing psychological mechanism of physical activity enhancing Chinese L2 learning efficacy with inhibiting aggressive behavior using cross-lagged panel model.PLoS One. 2025 Jun 3;20(6):e0324984. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0324984. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 40460393 Free PMC article.
-
Effectiveness of a Motor Intervention Program on Motivation and Learning of English Vocabulary in Preschoolers: A Pilot Study.Behav Sci (Basel). 2019 Aug 5;9(8):84. doi: 10.3390/bs9080084. Behav Sci (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31387261 Free PMC article.
-
Chain-mediated effect of physical activity between Chinese language-based L2 motivational self-system and intended effort.Sci Rep. 2025 Jan 26;15(1):3306. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-86517-7. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 39865115 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of a 10-Week Physical Activity Intervention on Asylum Seekers' Physiological Health.Brain Sci. 2022 Jun 24;12(7):822. doi: 10.3390/brainsci12070822. Brain Sci. 2022. PMID: 35884629 Free PMC article.
-
Interventions to improve refugee children's access to education and quality learning: A scoping review of existing impact evaluations.Int Rev Educ. 2023;69(1-2):227-247. doi: 10.1007/s11159-023-10004-2. Epub 2023 May 29. Int Rev Educ. 2023. PMID: 37313292 Free PMC article.
References
-
- United Nations Higher Commissioner for Refugees, editors. Global trends. Forced displacement in 2016 [Internet]. Geneva, Switzerland: Author; 2017 [cited 2017 Aug 27]. Available from: http://www.unhcr.org/5943e8a34.
-
- United Nations Higher Commissioner for Refugees, editors. Statistical Yearbook 2014. 14th ed. Geneva, Switzerland: Author; 2015.
-
- Massumi M, von Dewitz N, Grießbach J, Terhart H, Wagner K, Hippmann K et al., editors. Bestandsaufnahme und Empfehlungen Neu zugewanderte Kinder und Jugendliche im deutschen Schulsystem. Köln: Mercator; 2015.
-
- Ständige Konferenz der Kultusminister der Länder in der Bundesrepublik Deutschland. Interkulturelle Bildung und Erziehung in der Schule. Beschluss der Kultusministerkonferenz vom 25.10.1996 i.d.F. vom 05.12.2013 [Internet]. Bonn, Germany: Author; 1996 [cited 2017 Aug 23]. Available from: http://www.kmk.org/fileadmin/Dateien/veroeffentlichungen_beschluesse/199....
-
- Krüger M, Gebken U. Sportunterricht mit Seiteneinsteigern. Sportunterricht 2017;66(6):175–81.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources