Comparison of strain elastography, point shear wave elastography using acoustic radiation force impulse imaging and 2D-shear wave elastography for the differentiation of thyroid nodules
- PMID: 30222755
- PMCID: PMC6141102
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0204095
Comparison of strain elastography, point shear wave elastography using acoustic radiation force impulse imaging and 2D-shear wave elastography for the differentiation of thyroid nodules
Abstract
Purpose: The aim of the study was to compare three different elastography methods, namely Strain Elastography (SE), Point Shear-Wave Elastography (pSWE) using Acoustic Radiation Force Impulse (ARFI)-Imaging and 2D-Shear Wave Elastography (2D-SWE), in the same study population for the differentiation of thyroid nodules.
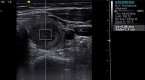
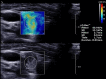
Materials and methods: All patients received a conventional ultrasound scan, SE and 2D-SWE, and all patients except for two received ARFI-Imaging. Cytology/histology of thyroid nodules was used as a reference method. SE measures the relative stiffness within the region of interest (ROI) using the surrounding tissue as reference tissue. ARFI mechanically excites the tissue at the ROI using acoustic pulses to generate localized tissue displacements. 2D-SWE measures tissue elasticity using the velocity of many shear waves as they propagate through the tissue.
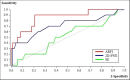
Results: 84 nodules (73 benign and 11 malignant) in 62 patients were analyzed. Sensitivity, specificity and NPV of SE were 73%, 70% and 94%, respectively. Sensitivity, specificity and NPV of ARFI and 2D-SWE were 90%, 79%, 98% and 73%, 67%, 94% respectively, using a cut-off value of 1.98m/s for ARFI and 2.65m/s (21.07kPa) for 2D-SWE. The AUROC (Area under the Receiver Operating Characteristic) of SE, ARFI and 2D-SWE for the diagnosis of malignant thyroid nodules were 52%, 86% and 71%, respectively. A significant difference in AUROC was found between SE and ARFI (p = 0.008), while no significant difference was found between ARFI and SWE (86% vs. 71%, p = 0.31), or SWE and SE (71% vs. 52%, p = 0.26).
Conclusion: pSWE using ARFI and 2D-SWE showed comparable results for the differentiation of thyroid nodules. ARFI was superior to elastography using SE.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Acoustic radiation force impulse induced strain elastography and point shear wave elastography for evaluation of thyroid nodules.Int J Clin Exp Med. 2015 Jul 15;8(7):10956-63. eCollection 2015. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2015. PMID: 26379890 Free PMC article.
-
Acoustic Radiation Force Impulse-Imaging for the evaluation of the thyroid gland: a limited patient feasibility study.Ultrasonics. 2012 Jan;52(1):69-74. doi: 10.1016/j.ultras.2011.06.012. Epub 2011 Jul 7. Ultrasonics. 2012. PMID: 21788057
-
Risk stratification of thyroid nodules with Bethesda category III results on fine-needle aspiration cytology: The additional value of acoustic radiation force impulse elastography.Oncotarget. 2017 Jan 3;8(1):1580-1592. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.13685. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 27906671 Free PMC article.
-
Quantitative Shear Wave Velocity Measurement on Acoustic Radiation Force Impulse Elastography for Differential Diagnosis between Benign and Malignant Thyroid Nodules: A Meta-analysis.Ultrasound Med Biol. 2015 Dec;41(12):3035-43. doi: 10.1016/j.ultrasmedbio.2015.08.003. Epub 2015 Sep 12. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2015. PMID: 26371402 Review.
-
Acoustic radiation force impulse imaging (ARFI) for differentiation of benign and malignant thyroid nodules--A meta-analysis.Eur J Radiol. 2015 Nov;84(11):2181-6. doi: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2015.07.015. Epub 2015 Jul 17. Eur J Radiol. 2015. PMID: 26259701 Review.
Cited by
-
Role of elastography strain ratio and TIRADS score in predicting malignant thyroid nodule.Arch Endocrinol Metab. 2021 May 18;64(6):735-742. doi: 10.20945/2359-3997000000283. Arch Endocrinol Metab. 2021. PMID: 34033283 Free PMC article.
-
Elastography of the thyroid nodule, cut-off points between benign and malignant lesions for strain, 2D shear wave real time and point shear wave: a correlation with pathology, ACR TIRADS and Alpha Score.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023 Jun 16;14:1182557. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1182557. eCollection 2023. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 37396172 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of thyroid nodules by shear wave elastography: a review of current knowledge.J Endocrinol Invest. 2021 Oct;44(10):2043-2056. doi: 10.1007/s40618-021-01570-z. Epub 2021 Apr 16. J Endocrinol Invest. 2021. PMID: 33864241 Review.
-
Role of Ultrasound Elastography and Contrast-Enhanced Ultrasound (CEUS) in Diagnosis and Management of Malignant Thyroid Nodules-An Update.Diagnostics (Basel). 2025 Mar 1;15(5):599. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics15050599. Diagnostics (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40075847 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Two-Dimensional Shear Wave Elastography of Normal Soft Tissue Organs in Adult Beagle Dogs; Interobserver Agreement and Sources of Variability.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2020 Aug 19;8:979. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2020.00979. eCollection 2020. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2020. PMID: 32974311 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Iannuccilli JD, Cronan JJ, Monchik JM. Risk for malignancy of thyroid nodules as assessed by sonographic criteria: the need for biopsy. J Ultrasound Med 2004; 23: 1455–1464 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

