Repurposing of Drugs Targeting YAP-TEAD Functions
- PMID: 30223434
- PMCID: PMC6162436
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers10090329
Repurposing of Drugs Targeting YAP-TEAD Functions
Abstract
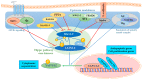
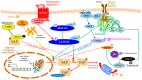
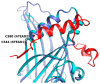
Drug repurposing is a fast and consolidated approach for the research of new active compounds bypassing the long streamline of the drug discovery process. Several drugs in clinical practice have been reported for modulating the major Hippo pathway's terminal effectors, namely YAP (Yes1-associated protein), TAZ (transcriptional co-activator with PDZ-binding motif) and TEAD (transcriptional enhanced associate domains), which are directly involved in the regulation of cell growth and tissue homeostasis. Since this pathway is known to have many cross-talking phenomena with cell signaling pathways, many efforts have been made to understand its importance in oncology. Moreover, this could be relevant to obtain new molecular tools and potential therapeutic assets. In this review, we discuss the main mechanisms of action of the best-known compounds, clinically approved or investigational drugs, able to cross-talk and modulate the Hippo pathway, as an attractive strategy for the discovery of new potential lead compounds.
Keywords: Hippo pathway; YAP-TEAD disruption; cell signaling; drug repurposing; protein-protein interactions.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

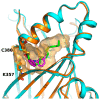
References
-
- Santucci M., Vignudelli T., Ferrari S., Mor M., Scalvini L., Bolognesi M.L., Uliassi E., Costi M.P. The Hippo Pathway and YAP/TAZ-TEAD Protein—Protein Interaction as Targets for Regenerative Medicine and Cancer Treatment: Miniperspective. J. Med. Chem. 2015;58:4857–4873. doi: 10.1021/jm501615v. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

