Individualized Transcriptional Resolution of Complicated Malaria in a Colombian Study
- PMID: 30223463
- PMCID: PMC6163772
- DOI: 10.3390/jpm8030029
Individualized Transcriptional Resolution of Complicated Malaria in a Colombian Study
Erratum in
-
Correction: Rojas-Peña et al. Individualized Transcriptional Resolution of Complicated Malaria in a Colombian Study. J. Pers. Med. 2018, 8, 29.J Pers Med. 2024 Oct 14;14(10):1060. doi: 10.3390/jpm14101060. J Pers Med. 2024. PMID: 39452575 Free PMC article.
Abstract
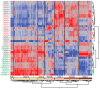
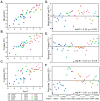
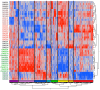
To evaluate whether recovery from complicated malaria follows a common trajectory in terms of immunological mechanism or, rather, is highly individualized for each patient, we performed longitudinal gene expression profiling of whole blood. RNA sequencing (RNAseq) was performed on blood samples obtained from eight patients on four consecutive days between hospital admission and discharge. Six patients were infected with Plasmodium falciparum, and two with Plasmodium vivax; one patient was a pregnant woman infected with P. falciparum, who was hospitalized for several weeks. The characterization of blood transcript modules (BTM) and blood informative transcripts (BIT) revealed that patients' responses showed little commonality, being dominated by the balance of gene activity relating to lymphocyte function, inflammation, and interferon responses specific to each patient. Only weak correlations with specific complicated malaria symptoms such as jaundice, thrombocytopenia, or anemia were observed. The differential expression of individual genes, including transcripts derived from the human leukocyte antigen (HLA) complex, generally reflected differences in the underlying immune processes. Although the results of this pilot study do not point to any single process that might provide a target for complicated malaria treatment or prevention or personalized medical strategies, larger patient series and more extensive blood sampling may allow the classification of patients according to their type of response in order to develop novel therapeutic approaches.
Keywords: Plasmodium; RNAseq; gene expression; longitudinal profiling; transcriptomics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- World Health Organization (WHO) World Malaria Report. WHO; Geneva, Switzerland: 2017.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

