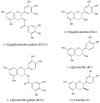
Effects of Tea Catechins on Alzheimer's Disease: Recent Updates and Perspectives
- PMID: 30223480
- PMCID: PMC6225145
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules23092357
Effects of Tea Catechins on Alzheimer's Disease: Recent Updates and Perspectives
Abstract
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is one of the most common neurodegenerative disorders worldwide. Its incidence is gradually increasing because of an aging demographic. Therefore, AD prevention and modification is important to improve the health status of older adults. Oxidative stress is a component of the pathological mechanisms underlying AD. It is caused by a disruption of the balance between reactive oxygen species and antioxidant molecules. This imbalance also causes neuroinflammation. Catechins, which are bioactive components of tea, have antioxidative and anti-inflammatory effects. Moreover, other potential properties related to AD prevention and modification have been reported in in vitro and in vivo studies. Several clinical studies have also been conducted to date. The current review summarizes recent updates and perspectives of the effects of catechins on AD based on the molecular mechanisms and related clinical studies.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; catechin; clinical study; molecular mechanisms.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Beneficial Effects of Green Tea Catechins on Neurodegenerative Diseases.Molecules. 2018 May 29;23(6):1297. doi: 10.3390/molecules23061297. Molecules. 2018. PMID: 29843466 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Multifunctional activities of green tea catechins in neuroprotection. Modulation of cell survival genes, iron-dependent oxidative stress and PKC signaling pathway.Neurosignals. 2005;14(1-2):46-60. doi: 10.1159/000085385. Neurosignals. 2005. PMID: 15956814 Review.
-
Association of Tea Consumption with Risk of Alzheimer's Disease and Anti-Beta-Amyloid Effects of Tea.Nutrients. 2018 May 22;10(5):655. doi: 10.3390/nu10050655. Nutrients. 2018. PMID: 29789466 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tea catechins prevent contractile dysfunction in unloaded murine soleus muscle: a pilot study.Nutrition. 2011 Sep;27(9):955-9. doi: 10.1016/j.nut.2010.10.008. Epub 2011 Jun 8. Nutrition. 2011. PMID: 21641774
-
Naturally occurring phytochemicals for the prevention of Alzheimer's disease.J Neurochem. 2010 Mar;112(6):1415-30. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2009.06562.x. Epub 2009 Dec 26. J Neurochem. 2010. PMID: 20050972 Review.
Cited by
-
Modulating Inflammation-Mediated Diseases via Natural Phenolic Compounds Loaded in Nanocarrier Systems.Pharmaceutics. 2023 Feb 19;15(2):699. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15020699. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 36840021 Free PMC article. Review.
-
PPAR and functional foods: Rationale for natural neurosteroid-based interventions for postpartum depression.Neurobiol Stress. 2020 Apr 19;12:100222. doi: 10.1016/j.ynstr.2020.100222. eCollection 2020 May. Neurobiol Stress. 2020. PMID: 32426424 Free PMC article.
-
Comprehensive Insights into Pathophysiology of Alzheimer's Disease: Herbal Approaches for Mitigating Neurodegeneration.Curr Alzheimer Res. 2024;21(9):625-648. doi: 10.2174/0115672050309057240404075003. Curr Alzheimer Res. 2024. PMID: 38623983 Review.
-
Natural Compounds for Preventing Age-Related Diseases and Cancers.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jul 9;25(14):7530. doi: 10.3390/ijms25147530. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39062777 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tieguanyin Oolong Tea Extracts Alleviate Behavioral Abnormalities by Modulating Neuroinflammation in APP/PS1 Mouse Model of Alzheimer's Disease.Foods. 2021 Dec 29;11(1):81. doi: 10.3390/foods11010081. Foods. 2021. PMID: 35010207 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alzheimer’s Association 2017 Alzheimer’s disease facts and figures. Alzheimers Dement. 2017;13:325–373. doi: 10.1016/j.jalz.2017.02.001. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical