Extended Targeted and Non-Targeted Strategies for the Analysis of Marine Toxins in Mussels and Oysters by (LC-HRMS)
- PMID: 30223487
- PMCID: PMC6162736
- DOI: 10.3390/toxins10090375
Extended Targeted and Non-Targeted Strategies for the Analysis of Marine Toxins in Mussels and Oysters by (LC-HRMS)
Abstract
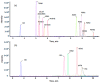
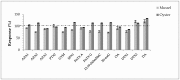
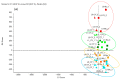
When considering the geographical expansion of marine toxins, the emergence of new toxins and the associated risk for human health, there is urgent need for versatile and efficient analytical methods that are able to detect a range, as wide as possible, of known or emerging toxins. Current detection methods for marine toxins rely on a priori defined target lists of toxins and are generally inappropriate for the detection and identification of emerging compounds. The authors describe the implementation of a recent approach for the non-targeted analysis of marine toxins in shellfish with a focus on a comprehensive workflow for the acquisition and treatment of the data generated after liquid chromatography coupled with high resolution mass spectrometry (LC-HRMS) analysis. First, the study was carried out in targeted mode to assess the performance of the method for known toxins with an extended range of polarities, including lipophilic toxins (okadaic acid, dinophysistoxins, azaspiracids, pectenotoxins, yessotoxins, cyclic imines, brevetoxins) and domoic acid. The targeted method, assessed for 14 toxins, shows good performance both in mussel and oyster extracts. The non-target potential of the method was then challenged via suspects and without a priori screening by blind analyzing mussel and oyster samples spiked with marine toxins. The data processing was optimized and successfully identified the toxins that were spiked in the blind samples.
Keywords: LC-HRMS; marine toxins; method characterization; non-targeted analysis; suspects screening; targeted analysis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The founding sponsors had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, and in the decision to publish the results.
Figures



References
-
- Frémy J.-M., Lassus P. Toxines d’Algues dans l’Alimentation. Ifremer; Issy-les-Moulineaux, France: 2001.
-
- UNESCO . Report of the Joint FAO/IOC/WHO ad hoc Expert Consultation on Biotoxins in Bivalve Molluscs. UNESCO; Oslo, Norway: 2005. Technical Report for UNESCO.
-
- Asakawa M. Marine Biotoxins: Occurrence, Toxicity, and Detection Methods. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2017 doi: 10.1088/1757-899X/193/1/012001. - DOI
-
- European Commission Commission Regulation No 786/2013 of 16th August 2013 amending Annex III to Regulation (EC) No 853/2004 of the European Parliament and of the Council as regards the permitted limits of yessotoxins in live bivalve molluscs Text with EEA relevance. Off. J. Eur. Union. 2013;220:14.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

