Mind the Gap: Mapping Mass Spectral Databases in Genome-Scale Metabolic Networks Reveals Poorly Covered Areas
- PMID: 30223552
- PMCID: PMC6161000
- DOI: 10.3390/metabo8030051
Mind the Gap: Mapping Mass Spectral Databases in Genome-Scale Metabolic Networks Reveals Poorly Covered Areas
Abstract
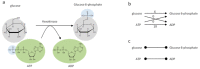
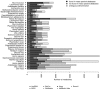
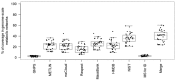
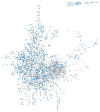
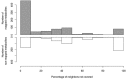
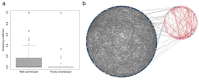
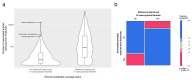
The use of mass spectrometry-based metabolomics to study human, plant and microbial biochemistry and their interactions with the environment largely depends on the ability to annotate metabolite structures by matching mass spectral features of the measured metabolites to curated spectra of reference standards. While reference databases for metabolomics now provide information for hundreds of thousands of compounds, barely 5% of these known small molecules have experimental data from pure standards. Remarkably, it is still unknown how well existing mass spectral libraries cover the biochemical landscape of prokaryotic and eukaryotic organisms. To address this issue, we have investigated the coverage of 38 genome-scale metabolic networks by public and commercial mass spectral databases, and found that on average only 40% of nodes in metabolic networks could be mapped by mass spectral information from standards. Next, we deciphered computationally which parts of the human metabolic network are poorly covered by mass spectral libraries, revealing gaps in the eicosanoids, vitamins and bile acid metabolism. Finally, our network topology analysis based on the betweenness centrality of metabolites revealed the top 20 most important metabolites that, if added to MS databases, may facilitate human metabolome characterization in the future.
Keywords: mass spectral libraries; metabolic networks; metabolite annotation; metabolomics data mapping.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
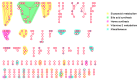
References
-
- Panopoulos A.D., Yanes O., Ruiz S., Kida Y.S., Diep D., Tautenhahn R., Herrerías A., Batchelder E.M., Plongthongkum N., Lutz M., et al. The metabolome of induced pluripotent stem cells reveals metabolic changes occurring in somatic cell reprogramming. Cell Res. 2012;22:168–177. doi: 10.1038/cr.2011.177. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

