The Early Recognition and Management of Sepsis in Sub-Saharan African Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 30223556
- PMCID: PMC6164025
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph15092017
The Early Recognition and Management of Sepsis in Sub-Saharan African Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
Sepsis is a common cause of morbidity and mortality in sub-Saharan African adults. Standardised management pathways have been documented to improve the survival of adults with sepsis from high-resource settings. Our aim was to assess the current evidence base for early sepsis interventions (recognition, empirical antibiotics, and resuscitation) in resource-poor settings of sub-Saharan Africa. We searched MEDLINE, EMBASE and CINHAL Plus databases to identify interventional studies for the early recognition and management of sepsis in sub-Saharan Africa (1 January 2000 to 1 August 2018) using a protocol-driven search strategy: adults, protocolised care pathway, and sub-Saharan Africa. We identified 725 publications of which three met criteria for final selection. Meta-analysis from two randomised controlled trials demonstrated that mortality was increased by 'early goal-directed therapy' interventions that increased fluid resuscitation (R.R. 1.26, 95% C.I. 1.00⁻1.58, p = 0.045; I² 53%). The third observational cohort study demonstrated improved survival after implementation of protocolised management for sepsis (mortality 33.0% vs. 45.7%, p = 0.005). No study incorporated standardised protocols for empirical antibiotic administration. High rates of pneumonia and mycobacteraemia were reported. There has been little research into the early recognition and management of sepsis in sub-Saharan Africa. Interventional trials of early goal-directed therapy have, to date, increased mortality. There is an urgent need to develop effective strategies to improve outcomes for adults with sepsis in sub-Saharan Africa.
Keywords: adults; pneumonia; protocolized care; sepsis; sub-Saharan Africa; tuberculosis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, and in the decision to publish the results.
Figures

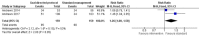
References
-
- Singer M., Deutschman C.S., Seymour C.W., Shankar-Hari M., Annane D., Bauer M., Bellomo R., Bernard G.R., Chiche J.D., Coopersmith C.M., et al. The third international consensus definitions for sepsis and septic shock (Sepsis-3) JAMA. 2016;315:801–810. doi: 10.1001/jama.2016.0287. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Vincent J.L., Marshall J.C., Namendys-Silva S.A., Francois B., Martin-Loeches I., Lipman J., Reinhart K., Antonelli M., Pickkers P., Njimi H., et al. Assessment of the worldwide burden of critical illness: The intensive care over nations (ICON) audit. Lancet Respir. Med. 2014;2:380–386. doi: 10.1016/S2213-2600(14)70061-X. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Rhodes A., Evans L.E., Alhazzani W., Levy M.M., Antonelli M., Ferrer R., Kumar A., Sevransky J.E., Sprung C.L., Nunnally M.E., et al. Surviving sepsis campaign: International guidelines for management of sepsis and septic shock: 2016. Intensive Care Med. 2017;43:304–377. doi: 10.1007/s00134-017-4683-6. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Levy M.M., Dellinger R.P., Townsend S.R., Linde-Zwirble W.T., Marshall J.C., Bion J., Schorr C., Artigas A., Ramsay G., Beale R., et al. The surviving sepsis campaign: Results of an international guideline-based performance improvement program targeting severe sepsis. Intensive Care Med. 2010;36:222–231. doi: 10.1007/s00134-009-1738-3. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

