Molecular Mechanism and Health Role of Functional Ingredients in Blueberry for Chronic Disease in Human Beings
- PMID: 30223619
- PMCID: PMC6164568
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms19092785
Molecular Mechanism and Health Role of Functional Ingredients in Blueberry for Chronic Disease in Human Beings
Abstract
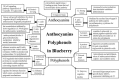
Functional ingredients in blueberry have the best health benefits. To obtain a better understanding of the health role of blueberry in chronic disease, we conducted systematic preventive strategies for functional ingredients in blueberry, based on comprehensive databases, especially PubMed, ISI Web of Science, and CNKI for the period 2008⁻2018. Blueberry is rich in flavonoids (mainly anthocyanidins), polyphenols (procyanidin), phenolic acids, pyruvic acid, chlorogenic acid, and others, which have anticancer, anti-obesity, prevent degenerative diseases, anti-inflammation, protective properties for vision and liver, prevent heart diseases, antidiabetes, improve brain function, protective lung properties, strong bones, enhance immunity, prevent cardiovascular diseases, and improve cognitive decline. The anthocyanins and polyphenols in blueberry are major functional ingredients for preventive chronic disease. These results support findings that blueberry may be one of the best functional fruits, and further reveals the mechanisms of anthocyanins and polyphenols in the health role of blueberry for chronic disease. This paper may be used as scientific evidence for developing functional foods, nutraceuticals, and novel drugs of blueberry for preventive chronic diseases.
Keywords: blueberry; chronic disease; functional food; functional ingredients.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Preventive and Therapeutic Role of Functional Ingredients of Barley Grass for Chronic Diseases in Human Beings.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2018 Apr 4;2018:3232080. doi: 10.1155/2018/3232080. eCollection 2018. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2018. PMID: 29849880 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Stability and biological activity of wild blueberry (Vaccinium angustifolium) polyphenols during simulated in vitro gastrointestinal digestion.Food Chem. 2014 Dec 15;165:522-31. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2014.05.135. Epub 2014 Jun 4. Food Chem. 2014. PMID: 25038707
-
Complex formation of blueberry (Vaccinium angustifolium) anthocyanins during freeze-drying and its influence on their biological activity.J Agric Food Chem. 2015 Mar 25;63(11):2935-46. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.5b00016. Epub 2015 Mar 13. J Agric Food Chem. 2015. PMID: 25727778
-
Comparison of phytochemical profiles, antioxidant and cellular antioxidant activities of different varieties of blueberry (Vaccinium spp.).Food Chem. 2017 Feb 15;217:773-781. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2016.09.002. Epub 2016 Sep 3. Food Chem. 2017. PMID: 27664697
-
Effects of blueberry and cranberry consumption on type 2 diabetes glycemic control: A systematic review.Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2019;59(11):1816-1828. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2018.1430019. Epub 2018 Feb 13. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2019. PMID: 29345498
Cited by
-
Two genes, ANS and UFGT2, from Vaccinium spp. are key steps for modulating anthocyanin production.Front Plant Sci. 2023 Feb 2;14:1082246. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2023.1082246. eCollection 2023. Front Plant Sci. 2023. PMID: 36818839 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of antioxidant supplement on immune health and physical wellbeing: A randomized, controlled trial.Adv Integr Med. 2022 Sep;9(3):180-184. doi: 10.1016/j.aimed.2022.06.007. Epub 2022 Jun 21. Adv Integr Med. 2022. PMID: 35757181 Free PMC article.
-
A 90 day oral toxicity study of blueberry polyphenols in ovariectomized sprague-dawley rats.Food Chem Toxicol. 2020 May;139:111254. doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2020.111254. Epub 2020 Mar 9. Food Chem Toxicol. 2020. PMID: 32165232 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison and interpretation of characteristics of Rhizosphere microbiomes of three blueberry varieties.BMC Microbiol. 2021 Jan 22;21(1):30. doi: 10.1186/s12866-021-02092-7. BMC Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 33482726 Free PMC article.
-
Chemical Composition, Antioxidant Activities, Antidepressant Effect, and Lipid Peroxidation of Peruvian Blueberry: Molecular Docking Studies on Targets Involved in Oxidative Stress and Depression.Plants (Basel). 2024 Jun 14;13(12):1643. doi: 10.3390/plants13121643. Plants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38931078 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Marhuenda J., Alemán M.D., Gironés-Vilaplana A., Pérez A., Caravaca G., Figueroa F., Mulero J., Zafrilla P. Phenolic composition, antioxidant activity, and in vitro availability of four different berries. J. Chem. 2016;2016:5194901. doi: 10.1155/2016/5194901. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical