Apparent diffusion coefficient as an effective index for the therapeutic efficiency of brain chemoradiotherapy for brain metastases from lung cancer
- PMID: 30223786
- PMCID: PMC6142399
- DOI: 10.1186/s12880-018-0275-3
Apparent diffusion coefficient as an effective index for the therapeutic efficiency of brain chemoradiotherapy for brain metastases from lung cancer
Abstract
Background: The potential of apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) value alteration before and after chemoradiotherapy as a potential monitor for therapeutic efficiency of treatment for brain metastases from lung cancer were discussed.
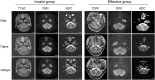
Method: Thirty lung cancer patients with brain metastases, conventional magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) examination and diffusion weighted imaging (DWI) were performed one week before chemoradiotherapy and after one treatment cycle and two treatment cycles. 43 tumor lesions were divided into effective group and invalid group according to the changes of the tumor size. The differences in ADC values at different time points before and after treatment in each treatment group were analyzed.
Result: The maximum diameter of the tumor was no difference after one treatment cycle, but decreased after two treatment cycles. ADC values significantly increased after both one and two treatment cycles. In effective group, the ADC values were significantly increased after one and two treatment cycles. While, there are no difference in invalid group after one treatment cycle but decreased after two treatment cycles. ΔADC values in effective group after one and two treatment cycles were both significantly higher than those in the invalid group. ROC curve analysis then revealed that the area under the curve (AUC) of ΔADC after one treatment was 0.872.
Conclusion: ADC values in brain metastases from lung cancer can help monitor and dynamically observe the therapeutic efficiency of whole brain chemoradiotherapy.
Keywords: Apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC); Brain metastases; Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI); Therapeutic efficiency.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki, and the protocol was approved by the Ethic Committee of The Third Affiliated Hospital of Beijing University of Chinese Medicine. All of the enrolled patients signed informed consent forms.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interest.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures


References
-
- Auperin A, Arriagada R, Pignon JP, Le Pechoux C, Gregor A, Stephens RJ, Kristjansen PE, Johnson BE, Ueoka H, Wagner H, et al. Prophylactic cranial irradiation for patients with small-cell lung cancer in complete remission. Prophylactic cranial irradiation overview collaborative group. N Engl J Med. 1999;341(7):476–484. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199908123410703. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Gore EM, Bae K, Wong SJ, Sun A, Bonner JA, Schild SE, Gaspar LE, Bogart JA, Werner-Wasik M, Choy H. Phase III comparison of prophylactic cranial irradiation versus observation in patients with locally advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: primary analysis of radiation therapy oncology group study RTOG 0214. J Clin Oncol. 2011;29(3):272–278. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2010.29.1609. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Brufsky AM, Mayer M, Rugo HS, Kaufman PA, Tan-Chiu E, Tripathy D, Tudor IC, Wang LI, Brammer MG, Shing M, et al. Central nervous system metastases in patients with HER2-positive metastatic breast cancer: incidence, treatment, and survival in patients from registHER. Clin Cancer Res. 2011;17(14):4834–4843. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-10-2962. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

