Reliability of ultrasonography to detect inflammatory lesions and structural damage in juvenile idiopathic arthritis
- PMID: 30223838
- PMCID: PMC6142317
- DOI: 10.1186/s12969-018-0275-4
Reliability of ultrasonography to detect inflammatory lesions and structural damage in juvenile idiopathic arthritis
Abstract
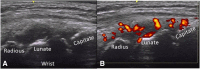
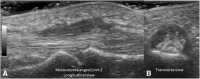
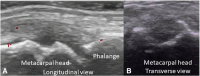
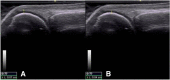
Background: Musculoskeletal Ultrasonography (MSUS) is an important tool for the clinical assessment in Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis (JIA). The objective of this study was to evaluate the reliability of MSUS to detect elementary lesions: synovitis, tenosynovitis, cartilage damage and bone erosions in the wrist and metacarpal (MCP) joints of patients with JIA.
Methods: Thirty children in various subgroups of JIA according to ILAR criteria, were included in this cross-sectional study. Clinical data including painful, swollen and limited joints were recorded. Five rheumatologist ultrasonographers, blinded to the clinical evaluation, evaluated the presence of elementary lesions in the wrist and MCP 2 and 3 joints bilaterally. The synovitis was graded in B-Mode and Power Doppler (PD). In addition to descriptive statistics intra- and inter-observer reliability was calculated using Cohen's kappa according to Landis and Koch.
Results: US detected more synovitis than the clinical examination (62% vs 28%, 30% vs 23% and 22% vs 17% in the wrist, second and third MCP joints respectively). The intra-observer concordance for synovitis in all joints was excellent in B-Mode (k 0.84 .63-1.0 p = 0.001), except for MCP 2, where it was good (0.61, IC 95% .34-89, p = 0.001). For both modalities (PD, B-Mode) tenosynovitis, cartilage damage and bone erosions it was also excellent. Regarding synovitis grading the concordance was excellent for all grades (0.83-1.0, IC 95% 0.51.1.0, p = 0.001), except for grade 1 where it was good (0.61, IC 95% 0.43-.83, p = 0.001). Reliability inter-observer for grayscale synovitis (0.67-0.95, IC 95% 0.67-1.0, p = 0.001), tenosynovitis grayscale (0.89, IC 95% 0.78-0.99, p.001), damage cartilage (0.89, IC 95% 0.78-0.99, p = 0.001), PD (0.66, IC 95% 0.39-1.0, p = 0.001). The concordance for grading synovitis was excellent, but for grayscale grade 1 and 2 (.66, IC 95% .53-.74, p = 0.007) and PD grade 1 and 2 (0.63, IC 95% .58-.91, p = 004) was good.
Conclusions: The intra- and inter-observer reliability of MSUS for inflammatory and structural lesions is good to excellent for the wrist and MCP in patients with JIA.
Keywords: Juvenile idiopathic arthritis; Musculoskeletal ultrasound; Reliability.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Trial registration 52/16 ethics committee National Institute of Rehabilitation in México city.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
References
-
- Colebatch-Bourn AN, Edwards CJ, Collado P, D'Agostino MA, Hemke R, Jousse-Joulin S, et al. EULAR-PReS points to consider for the use of imaging in the diagnosis and management of juvenile idiopathic arthritis in clinical practice. Ann Rheum Dis. 2015;74:1946–1957. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2015-207892. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Filippou G, Cantarini L, Bertoli I, Picerno V, Frediani B, Galeazzi M. Ultrasonography vs. clinical examination in children with suspected arthritis. Does it make sense to use poliarticular ultrasonographic screening? Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2011;29:345–350. - PubMed
-
- Laurell L, Court-Payen M, Nielsen S, Zak M, Boesen M, Fasth A. Ultrasonography and color Doppler in juvenile idiopathic arthritis: diagnosis and follow-up of ultrasound-guided steroid injection in the ankle region. A descriptive interventional study. Pediatr Rheumatol Online. 2011;9:4. doi: 10.1186/1546-0096-9-4. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

