Therapeutic Potential of Mesenchymal Cell-Derived miRNA-150-5p-Expressing Exosomes in Rheumatoid Arthritis Mediated by the Modulation of MMP14 and VEGF
- PMID: 30224512
- PMCID: PMC6176104
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.1800304
Therapeutic Potential of Mesenchymal Cell-Derived miRNA-150-5p-Expressing Exosomes in Rheumatoid Arthritis Mediated by the Modulation of MMP14 and VEGF
Abstract
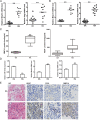
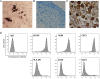
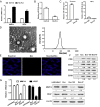
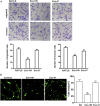
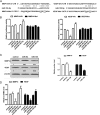
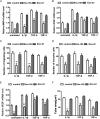
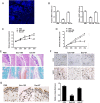
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic autoimmune disease characterized by synovial tissue inflammation and joint destruction associated with the activation of angiogenesis. Exosomes, which play a role in cell-to-cell communication as carriers of genetic information, transfer microRNAs (miRNAs or miRs) between cells and have been studied as delivery vehicles for therapeutic molecules. The aim of the current study was to investigate the therapeutic effect of mesenchymal stem cell (MSC)-derived miR-150-5p exosomes on joint destruction in RA. The expression and secretion of miR-150-5p, matrix metalloproteinase (MMP) 14, and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) in RA patients and fibroblast-like synoviocytes (FLS) were examined by quantitative RT-PCR, ELISA, and Western blotting. Immunohistochemistry was used to assess angiogenesis. MSCs were transfected with an miR-150-5p expression plasmid, and MSC-derived exosomes were harvested. The effect of MSC-derived miR-150-5p exosomes (Exo-150) on MMP14 and VEGF expression was examined. The effects of Exo-150 on cell migration and invasion in cytokine-stimulated FLS from RA patients were examined by HUVEC tube formation and transwell assays. The effect of Exo-150 in vivo was examined in a collagen-induced arthritis mouse model. Exo-150 decreased migration and invasion in RA FLS and downregulated tube formation in HUVECs by targeting MMP14 and VEGF. Injection of Exo-150 reduced hind paw thickness and the clinical arthritic scores in collagen-induced arthritis mice. Exo-150 reduced joint destruction by inhibiting synoviocyte hyperplasia and angiogenesis. Exosomes facilitate the direct intracellular transfer of miRNAs between cells and represent a potential therapeutic strategy for RA.
Copyright © 2018 by The American Association of Immunologists, Inc.
Figures
Similar articles
-
TNF-α stimulated exosome derived from fibroblast-like synoviocytes isolated from rheumatoid arthritis patients promotes HUVEC migration, invasion and angiogenesis by targeting the miR-200a-3p/KLF6/VEGFA axis.Autoimmunity. 2023 Dec;56(1):2282939. doi: 10.1080/08916934.2023.2282939. Epub 2023 Nov 17. Autoimmunity. 2023. PMID: 37975481
-
Resolvin D1 suppresses pannus formation via decreasing connective tissue growth factor caused by upregulation of miRNA-146a-5p in rheumatoid arthritis.Arthritis Res Ther. 2020 Mar 27;22(1):61. doi: 10.1186/s13075-020-2133-2. Arthritis Res Ther. 2020. PMID: 32216830 Free PMC article.
-
Amelioration of Experimental Autoimmune Arthritis Through Targeting of Synovial Fibroblasts by Intraarticular Delivery of MicroRNAs 140-3p and 140-5p.Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016 Feb;68(2):370-81. doi: 10.1002/art.39446. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016. PMID: 26473405
-
New Therapeutic Strategies for the Inflammatory Rheumatoid Arthritis Disease: Emphasizing Mesenchymal Stem Cells and Associated exo-miRNA or exo-lncRNA.Cell Biochem Biophys. 2024 Sep;82(3):1599-1611. doi: 10.1007/s12013-024-01316-7. Epub 2024 May 31. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2024. PMID: 38822204 Review.
-
Wnt signaling pathway in rheumatoid arthritis, with special emphasis on the different roles in synovial inflammation and bone remodeling.Cell Signal. 2013 Oct;25(10):2069-78. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2013.04.002. Epub 2013 Apr 17. Cell Signal. 2013. PMID: 23602936 Review.
Cited by
-
Updates on the Pathophysiology and Therapeutic Potential of Extracellular Vesicles with Focus on Exosomes in Rheumatoid Arthritis.J Inflamm Res. 2024 Jul 19;17:4811-4826. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S465653. eCollection 2024. J Inflamm Res. 2024. PMID: 39051053 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Extracellular vesicle-based Nanotherapeutics: Emerging frontiers in anti-inflammatory therapy.Theranostics. 2020 Jul 9;10(18):8111-8129. doi: 10.7150/thno.47865. eCollection 2020. Theranostics. 2020. PMID: 32724461 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MicroRNA-23a-5p regulates cell proliferation, migration and inflammation of TNF-α-stimulated human fibroblast-like MH7A synoviocytes by targeting TLR4 in rheumatoid arthritis.Exp Ther Med. 2021 May;21(5):479. doi: 10.3892/etm.2021.9910. Epub 2021 Mar 12. Exp Ther Med. 2021. PMID: 33767774 Free PMC article.
-
Update on the role of extracellular vesicles in rheumatoid arthritis.Expert Rev Mol Med. 2022 Mar 17;24:e12. doi: 10.1017/erm.2021.33. Expert Rev Mol Med. 2022. PMID: 35297366 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Angioregulatory microRNAs in Colorectal Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2019 Dec 26;12(1):71. doi: 10.3390/cancers12010071. Cancers (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31887997 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Scott D. L., Wolfe F., Huizinga T. W. 2010. Rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet 376: 1094–1108. - PubMed
-
- Sabeh F., Fox D., Weiss S. J. 2010. Membrane-type I matrix metalloproteinase-dependent regulation of rheumatoid arthritis synoviocyte function. J. Immunol. 184: 6396–6406. - PubMed
-
- Wang C. H., Yao H., Chen L. N., Jia J. F., Wang L., Dai J. Y., Zheng Z. H., Chen Z. N., Zhu P. 2012. CD147 induces angiogenesis through a vascular endothelial growth factor and hypoxia-inducible transcription factor 1α-mediated pathway in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 64: 1818–1827. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

