Therapeutic Potential of Mesenchymal Cell-Derived miRNA-150-5p-Expressing Exosomes in Rheumatoid Arthritis Mediated by the Modulation of MMP14 and VEGF
- PMID: 30224512
- PMCID: PMC6176104
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.1800304
Therapeutic Potential of Mesenchymal Cell-Derived miRNA-150-5p-Expressing Exosomes in Rheumatoid Arthritis Mediated by the Modulation of MMP14 and VEGF
Abstract
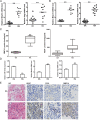
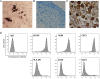
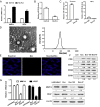
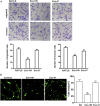
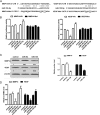
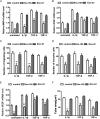
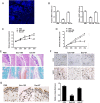
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic autoimmune disease characterized by synovial tissue inflammation and joint destruction associated with the activation of angiogenesis. Exosomes, which play a role in cell-to-cell communication as carriers of genetic information, transfer microRNAs (miRNAs or miRs) between cells and have been studied as delivery vehicles for therapeutic molecules. The aim of the current study was to investigate the therapeutic effect of mesenchymal stem cell (MSC)-derived miR-150-5p exosomes on joint destruction in RA. The expression and secretion of miR-150-5p, matrix metalloproteinase (MMP) 14, and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) in RA patients and fibroblast-like synoviocytes (FLS) were examined by quantitative RT-PCR, ELISA, and Western blotting. Immunohistochemistry was used to assess angiogenesis. MSCs were transfected with an miR-150-5p expression plasmid, and MSC-derived exosomes were harvested. The effect of MSC-derived miR-150-5p exosomes (Exo-150) on MMP14 and VEGF expression was examined. The effects of Exo-150 on cell migration and invasion in cytokine-stimulated FLS from RA patients were examined by HUVEC tube formation and transwell assays. The effect of Exo-150 in vivo was examined in a collagen-induced arthritis mouse model. Exo-150 decreased migration and invasion in RA FLS and downregulated tube formation in HUVECs by targeting MMP14 and VEGF. Injection of Exo-150 reduced hind paw thickness and the clinical arthritic scores in collagen-induced arthritis mice. Exo-150 reduced joint destruction by inhibiting synoviocyte hyperplasia and angiogenesis. Exosomes facilitate the direct intracellular transfer of miRNAs between cells and represent a potential therapeutic strategy for RA.
Copyright © 2018 by The American Association of Immunologists, Inc.
Figures
References
-
- Scott D. L., Wolfe F., Huizinga T. W. 2010. Rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet 376: 1094–1108. - PubMed
-
- Sabeh F., Fox D., Weiss S. J. 2010. Membrane-type I matrix metalloproteinase-dependent regulation of rheumatoid arthritis synoviocyte function. J. Immunol. 184: 6396–6406. - PubMed
-
- Wang C. H., Yao H., Chen L. N., Jia J. F., Wang L., Dai J. Y., Zheng Z. H., Chen Z. N., Zhu P. 2012. CD147 induces angiogenesis through a vascular endothelial growth factor and hypoxia-inducible transcription factor 1α-mediated pathway in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 64: 1818–1827. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

