APOBEC3H Subcellular Localization Determinants Define Zipcode for Targeting HIV-1 for Restriction
- PMID: 30224517
- PMCID: PMC6234287
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.00356-18
APOBEC3H Subcellular Localization Determinants Define Zipcode for Targeting HIV-1 for Restriction
Abstract
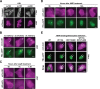
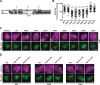
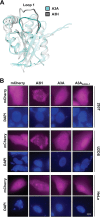
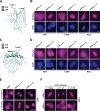
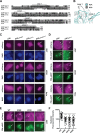
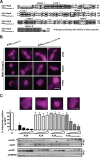
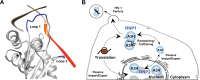
APOBEC enzymes are DNA cytosine deaminases that normally serve as virus restriction factors, but several members, including APOBEC3H, also contribute to cancer mutagenesis. Despite their importance in multiple fields, little is known about cellular processes that regulate these DNA mutating enzymes. We show that APOBEC3H exists in two distinct subcellular compartments, cytoplasm and nucleolus, and that the structural determinants for each mechanism are genetically separable. First, native and fluorescently tagged APOBEC3Hs localize to these two compartments in multiple cell types. Second, a series of genetic, pharmacologic, and cell biological studies demonstrate active cytoplasmic and nucleolar retention mechanisms, whereas nuclear import and export occur through passive diffusion. Third, APOBEC3H cytoplasmic retention determinants relocalize APOBEC3A from a passive cell-wide state to the cytosol and, additionally, endow potent HIV-1 restriction activity. These results indicate that APOBEC3H has a structural zipcode for subcellular localization and selecting viral substrates for restriction.
Keywords: APOBEC3H; DNA deamination; cancer mutagenesis; cytoplasmic retention; nuclear import; retrovirus restriction; subcellular localization.
Copyright © 2018 American Society for Microbiology.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Polymorphism in human APOBEC3H affects a phenotype dominant for subcellular localization and antiviral activity.J Virol. 2011 Aug;85(16):8197-207. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00624-11. Epub 2011 Jun 8. J Virol. 2011. PMID: 21653666 Free PMC article.
-
The Antiviral and Cancer Genomic DNA Deaminase APOBEC3H Is Regulated by an RNA-Mediated Dimerization Mechanism.Mol Cell. 2018 Jan 4;69(1):75-86.e9. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.12.010. Epub 2017 Dec 28. Mol Cell. 2018. PMID: 29290613 Free PMC article.
-
Flexibility in Nucleic Acid Binding Is Central to APOBEC3H Antiviral Activity.J Virol. 2019 Nov 26;93(24):e01275-19. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01275-19. Print 2019 Dec 15. J Virol. 2019. PMID: 31578294 Free PMC article.
-
Natural Polymorphisms and Oligomerization of Human APOBEC3H Contribute to Single-stranded DNA Scanning Ability.J Biol Chem. 2015 Nov 6;290(45):27188-27203. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M115.666065. Epub 2015 Sep 22. J Biol Chem. 2015. PMID: 26396192 Free PMC article.
-
APOBEC3B Nuclear Localization Requires Two Distinct N-Terminal Domain Surfaces.J Mol Biol. 2018 Aug 17;430(17):2695-2708. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2018.04.044. Epub 2018 May 19. J Mol Biol. 2018. PMID: 29787764 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Polymorphisms in Human APOBEC3H Differentially Regulate Ubiquitination and Antiviral Activity.Viruses. 2020 Mar 30;12(4):378. doi: 10.3390/v12040378. Viruses. 2020. PMID: 32235597 Free PMC article.
-
Competition for DNA binding between the genome protector replication protein A and the genome modifying APOBEC3 single-stranded DNA deaminases.Nucleic Acids Res. 2022 Nov 28;50(21):12039-12057. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkac1121. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022. PMID: 36444883 Free PMC article.
-
Single-nucleotide polymorphism of the DNA cytosine deaminase APOBEC3H haplotype I leads to enzyme destabilization and correlates with lung cancer.NAR Cancer. 2020 Sep;2(3):zcaa023. doi: 10.1093/narcan/zcaa023. Epub 2020 Sep 17. NAR Cancer. 2020. PMID: 32984821 Free PMC article.
-
Highly-potent, synthetic APOBEC3s restrict HIV-1 through deamination-independent mechanisms.PLoS Pathog. 2021 Jun 25;17(6):e1009523. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1009523. eCollection 2021 Jun. PLoS Pathog. 2021. PMID: 34170969 Free PMC article.
-
Small Molecule Inhibitors of Activation-Induced Deaminase Decrease Class Switch Recombination in B Cells.ACS Pharmacol Transl Sci. 2021 May 7;4(3):1214-1226. doi: 10.1021/acsptsci.1c00064. eCollection 2021 Jun 11. ACS Pharmacol Transl Sci. 2021. PMID: 34151211 Free PMC article.
References
-
- LaRue RS, Andrésdóttir V, Blanchard Y, Conticello SG, Derse D, Emerman M, Greene WC, Jónsson SR, Landau NR, Löchelt M, Malik HS, Malim MH, Münk C, O'Brien SJ, Pathak VK, Strebel K, Wain-Hobson S, Yu XF, Yuhki N, Harris RS. 2009. Guidelines for naming nonprimate APOBEC3 genes and proteins. J Virol 83:494–497. doi:10.1128/JVI.01976-08. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
