Fine-mapping and functional studies highlight potential causal variants for rheumatoid arthritis and type 1 diabetes
- PMID: 30224649
- PMCID: PMC6364548
- DOI: 10.1038/s41588-018-0216-7
Fine-mapping and functional studies highlight potential causal variants for rheumatoid arthritis and type 1 diabetes
Abstract
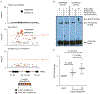
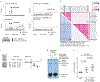
To define potentially causal variants for autoimmune disease, we fine-mapped1,2 76 rheumatoid arthritis (11,475 cases, 15,870 controls)3 and type 1 diabetes loci (9,334 cases, 11,111 controls)4. After sequencing 799 1-kilobase regulatory (H3K4me3) regions within these loci in 568 individuals, we observed accurate imputation for 89% of common variants. We defined credible sets of ≤5 causal variants at 5 rheumatoid arthritis and 10 type 1 diabetes loci. We identified potentially causal missense variants at DNASE1L3, PTPN22, SH2B3, and TYK2, and noncoding variants at MEG3, CD28-CTLA4, and IL2RA. We also identified potential candidate causal variants at SIRPG and TNFAIP3. Using functional assays, we confirmed allele-specific protein binding and differential enhancer activity for three variants: the CD28-CTLA4 rs117701653 SNP, MEG3 rs34552516 indel, and TNFAIP3 rs35926684 indel.
Figures
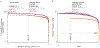
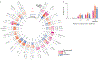

Comment in
-
Potential causal variants for RA identified.Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2018 Nov;14(11):621. doi: 10.1038/s41584-018-0103-8. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2018. PMID: 30315243 No abstract available.
References
-
- Klareskog L, Catrina AI & Paget S Rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet 373, 659–672 (2009). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

