Ring synthetic chromosome V SCRaMbLE
- PMID: 30224715
- PMCID: PMC6141504
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-018-06216-y
Ring synthetic chromosome V SCRaMbLE
Abstract
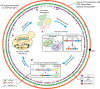
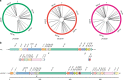
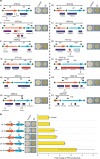
Structural variations (SVs) exert important functional impacts on biological phenotypic diversity. Here we show a ring synthetic yeast chromosome V (ring_synV) can be used to continuously generate complex genomic variations and improve the production of prodeoxyviolacein (PDV) by applying Synthetic Chromosome Recombination and Modification by LoxP-mediated Evolution (SCRaMbLE) in haploid yeast cells. The SCRaMbLE of ring_synV generates aneuploid yeast strains with increased PDV productivity, and we identify aneuploid chromosome I, III, VI, XII, XIII, and ring_synV. The neochromosome of SCRaMbLEd ring_synV generated more unbalanced forms of variations, including duplication, insertions, and balanced forms of translocations and inversions than its linear form. Furthermore, of the 29 novel SVs detected, 11 prompted the PDV biosynthesis; and the deletion of uncharacterized gene YER182W is related to the improvement of the PDV. Overall, the SCRaMbLEing ring_synV embraces the evolution of the genome by modifying the chromosome number, structure, and organization, identifying targets for phenotypic comprehension.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
SCRaMbLE generates evolved yeasts with increased alkali tolerance.Microb Cell Fact. 2019 Mar 11;18(1):52. doi: 10.1186/s12934-019-1102-4. Microb Cell Fact. 2019. PMID: 30857530 Free PMC article.
-
SCRaMbLE-in: A Fast and Efficient Method to Diversify and Improve the Yields of Heterologous Pathways in Synthetic Yeast.Methods Mol Biol. 2020;2205:305-327. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-0908-8_17. Methods Mol Biol. 2020. PMID: 32809206
-
Synthetic chromosome arms function in yeast and generate phenotypic diversity by design.Nature. 2011 Sep 14;477(7365):471-6. doi: 10.1038/nature10403. Nature. 2011. PMID: 21918511 Free PMC article.
-
Discovering and genotyping genomic structural variations by yeast genome synthesis and inducible evolution.FEMS Yeast Res. 2020 Mar 1;20(2):foaa012. doi: 10.1093/femsyr/foaa012. FEMS Yeast Res. 2020. PMID: 32188997 Review.
-
Probing eukaryotic genome functions with synthetic chromosomes.Exp Cell Res. 2020 May 1;390(1):111936. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2020.111936. Epub 2020 Mar 9. Exp Cell Res. 2020. PMID: 32165165 Review.
Cited by
-
Practical Approaches for the Yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae Genome Modification.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jul 26;24(15):11960. doi: 10.3390/ijms241511960. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37569333 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Enhancement and mapping of tolerance to salt stress and 5-fluorocytosine in synthetic yeast strains via SCRaMbLE.Synth Syst Biotechnol. 2022 Apr 16;7(3):869-877. doi: 10.1016/j.synbio.2022.04.003. eCollection 2022 Sep. Synth Syst Biotechnol. 2022. PMID: 35601823 Free PMC article.
-
Large-scale genomic rearrangements boost SCRaMbLE in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Nat Commun. 2024 Jan 26;15(1):770. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-44511-5. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 38278805 Free PMC article.
-
Synthetic biology for evolutionary engineering: from perturbation of genotype to acquisition of desired phenotype.Biotechnol Biofuels. 2019 May 9;12:113. doi: 10.1186/s13068-019-1460-5. eCollection 2019. Biotechnol Biofuels. 2019. PMID: 31086565 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Synthetic evolution of Saccharomyces cerevisiae for biomanufacturing: Approaches and applications.mLife. 2025 Feb 23;4(1):1-16. doi: 10.1002/mlf2.12167. eCollection 2025 Feb. mLife. 2025. PMID: 40026576 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 21621004/National Natural Science Foundation of China (National Science Foundation of China)/International
- 21750001/National Natural Science Foundation of China (National Science Foundation of China)/International
- 2014CB745100/Ministry of Science and Technology of the People's Republic of China (Chinese Ministry of Science and Technology)/International
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

