Role of Histamine in Modulating the Immune Response and Inflammation
- PMID: 30224900
- PMCID: PMC6129797
- DOI: 10.1155/2018/9524075
Role of Histamine in Modulating the Immune Response and Inflammation
Abstract
Inflammatory mediators, including cytokines, histamine, bradykinin, prostaglandins, and leukotrienes, impact the immune system, usually as proinflammatory factors. Other mediators act as regulatory components to establish homeostasis after injury or prevent the inflammatory process. Histamine, a biogenic vasoactive amine, causes symptoms such as allergies and has a pleiotropic effect that is dependent on its interaction with its four histamine receptors. In this review, we discuss the dualistic effects of histamine: how histamine affects inflammation of the immune system through the activation of intracellular pathways that induce the production of inflammatory mediators and cytokines in different immune cells and how histamine exerts regulatory functions in innate and adaptive immune responses. We also evaluate the interactions between these effects.
Figures
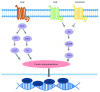
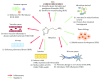
References
-
- Biegański T. Biochemical, physiological and pathophysiological aspects of intestinal diamine oxidase. Acta Physiologica Polonica. 1983;34(1):139–154. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

