Potential Effect of Exosomes Derived from Cancer Stem Cells and MSCs on Progression of DEN-Induced HCC in Rats
- PMID: 30224923
- PMCID: PMC6129855
- DOI: 10.1155/2018/8058979
Potential Effect of Exosomes Derived from Cancer Stem Cells and MSCs on Progression of DEN-Induced HCC in Rats
Abstract
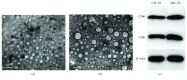
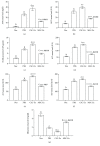
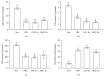
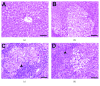
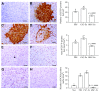
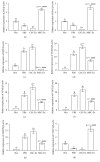
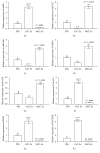
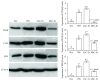
Cross talk, mediated by exosomes, between normal stem cells and cancer stem cells (CSCs) in the tumor microenvironment has been given less attention so far. In addition, no publications are available in the literature that address the in vivo impact of exosomes derived from CSCs and mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) on progression of long-term hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Herein, we hypothesized that transfer of exosomes among the cells in the HCC microenvironment could either induce or inhibit tumor growth and metastasis depending on their source. To check this hypothesis, we investigated the effect of exosomes coming from two different stem cell populations, hepatic CSCs and bone marrow (BM) MSCs, on progression of long-term DEN-induced HCC in rats and the involved underlying mechanisms. CSCs-exosomes induced a significant increase in liver relative weight and serum levels of cancer markers (AFP and GGT) and liver enzymes (ALT, AST, and ALP), intensive immunostaining for the HCC marker GST-P, and an increased number and area of tumor nodules as compared to HCC rats injected by PBS. CSCs-exosomes also decreased apoptosis (marked by downregulation of Bax and p53 and upregulation of Bcl2, and increased immunostaining of PCNA), increased angiogenetic activity (revealed by upregulation of VEGF), enhanced metastasis and invasiveness (indicated by upregulation of P13K and ERK proteins and their downstream target MMP9 and downregulation of TIMP1), and induced epithelial mesenchymal transition (marked by increased serum and hepatic level of TGFβ1 mRNA and protein). Notably, CSCs-exosomes also elevated HCC exosomal microRNA (miR) 21, exosomal long noncoding (lnc) RNA Tuc339, lncHEIH, and the HCC lncHOTAIR and decreased liver miR122 and HCC miRs (miR148a, miR16, and miR125b). All these cellular, functional, and molecular changes were reversed following injection of BM-MSCs-exosomes. However, both CSCs- and MSCs-exosomes failed to change the elevated oxidative stress or the inhibited antioxidant activities induced by HCC. Collectively, our results revealed a tumor stimulatory effect (induction of tumor growth, progression, and metastasis) for exosomes derived from CSCs and an inhibitory effect for exosomes derived from MSCs. These results provide valuable insight on the effect of CSCs- and MSCs-exosomes on HCC growth and progression in vivo, which may be helpful to understand the mechanism of HCC development.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Exosomes from BM-MSCs increase the population of CSCs via transfer of miR-142-3p.Br J Cancer. 2018 Sep;119(6):744-755. doi: 10.1038/s41416-018-0254-z. Epub 2018 Sep 17. Br J Cancer. 2018. PMID: 30220706 Free PMC article.
-
The potential therapeutic effect for melatonin and mesenchymal stem cells on hepatocellular carcinoma.Biomedicine (Taipei). 2019 Dec;9(4):24. doi: 10.1051/bmdcn/2019090424. Epub 2019 Nov 14. Biomedicine (Taipei). 2019. PMID: 31724939 Free PMC article.
-
Melatonin maximizes the therapeutic potential of non-preconditioned MSCs in a DEN-induced rat model of HCC.Biomed Pharmacother. 2019 Jun;114:108732. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2019.108732. Epub 2019 Mar 27. Biomed Pharmacother. 2019. PMID: 30925457
-
The role of extracellular vesicles in mediating progression, metastasis and potential treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma.Oncotarget. 2017 Jan 10;8(2):3683-3695. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.12465. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 27713136 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of Mesenchymal Stem Cells in the Induction of Cancer-Stem Cell Phenotype.Front Oncol. 2022 Feb 17;12:817971. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.817971. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35251985 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Epsilon-caprolactone-modified polyethylenimine as a genetic vehicle for stem cell-based bispecific antibody and exosome synergistic therapy.Regen Biomater. 2022 Nov 2;10:rbac090. doi: 10.1093/rb/rbac090. eCollection 2023. Regen Biomater. 2022. PMID: 36683744 Free PMC article.
-
Exosomal Non-Coding RNAs: New Insights into the Biology of Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Curr Oncol. 2022 Jul 29;29(8):5383-5406. doi: 10.3390/curroncol29080427. Curr Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36005165 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Long noncoding RNA NEAT1 changes exosome secretion and microRNA expression carried by exosomes in hepatocellular carcinoma cells.J Gastrointest Oncol. 2021 Dec;12(6):3033-3049. doi: 10.21037/jgo-21-729. J Gastrointest Oncol. 2021. PMID: 35070428 Free PMC article.
-
Involvement of lncRNAs and Macrophages: Potential Regulatory Link to Angiogenesis.J Immunol Res. 2020 Feb 29;2020:1704631. doi: 10.1155/2020/1704631. eCollection 2020. J Immunol Res. 2020. PMID: 32190702 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exosomal microRNA-15a from mesenchymal stem cells impedes hepatocellular carcinoma progression via downregulation of SALL4.Cell Death Discov. 2021 Aug 28;7(1):224. doi: 10.1038/s41420-021-00611-z. Cell Death Discov. 2021. PMID: 34455417 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

