SYKT Alleviates Doxorubicin-Induced Cardiotoxicity via Modulating ROS-Mediated p53 and MAPK Signal Pathways
- PMID: 30224925
- PMCID: PMC6129364
- DOI: 10.1155/2018/2581031
SYKT Alleviates Doxorubicin-Induced Cardiotoxicity via Modulating ROS-Mediated p53 and MAPK Signal Pathways
Abstract
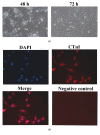
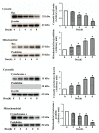
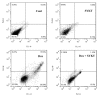
Backgrounds. Doxorubicin (DOX) is an effective therapeutic drug for malignant tumors; however, its clinical applications were limited by its side effects, especially the cardiotoxicity caused by ROS-mediated p53 and MAPK signal pathways' activation-induced cell apoptosis. Sanyang Xuedai mixture (SYKT) has been reported as an antioxidant agent and attenuated DOX-induced cardiotoxicity by targeting ROS-mediated apoptosis, but the mechanisms are still not fully delineated. Objective. This study aimed at investigating whether SYKT alleviated DOX-induced cardiotoxicity by inhibiting ROS-mediated apoptosis and elucidating the role of ROS-mediated p53 and MAPK signal pathways' activation in this process. Materials and Methods. Identification, separation, and culture of mouse primary cardiomyocytes. Cells were treated with DOX (1 μM), SYKT (30 mg/mL), or SYKT coupled with DOX. The p53 inhibitor Pifithrin-α (PFT-α), p38/MAPK inhibitor SB203583 (SB), and JNK inhibitor SP600125 (SP) were used as positive control. Western blot was employed to detected p53 and p38 as well as JNK expressions and the activation and translocation of Bax and cytochrome C. Flow cytometer (FCM) was used to detect the mitochondrial membrane potential and cell apoptosis. Results. After separation and culture, 95% of cells showed positive cTnI expression, which indicated that mouse primary cardiomyocytes were successfully identified in our research. DOX activated p53 and MAPK signal pathways in a time-dependent manner, which were inactivated by being cotreated with SYKT, PFT-α, or SB, respectively. DOX significantly decreased Bax and increased cytochrome c expressions in the cytoplasm, whereas Bax was upregulated and cytochrome c was downregulated in the mitochondria, which were reversed by SYKT treatment. Besides, DOX reduced mitochondria membrane potential (MMP) in cardiomyocytes compared to the control group; SYKT recovered its MMP and attenuated DOX-induced cardiomyocyte injury. Of note, DOX increased the expression levels of cleaved caspase-3 as well as poly ADP-ribose polymerase (PARP) and promoted cell apoptosis, which were also reversed by SYKT treatment. Discussion and Conclusions. Our results indicated that SYKT alleviated DOX-induced cardiotoxicity by inhibiting p53 and MAPK signal pathways' activation-mediated apoptosis, and it might serve as a potential therapeutic agent for DOX-induced cardiotoxicity.
Figures




References
-
- Carresi C., Musolino V., Gliozzi M., et al. Anti-oxidant effect of bergamot polyphenolic fraction counteracts doxorubicin-induced cardiomyopathy: Role of autophagy and c-kit pos CD45 neg CD31 neg cardiac stem cell activation. Journal of Molecular and Cellular Cardiology. 2018;119:10–18. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2018.04.007. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Wei X., Liu L., Guo X., Wang Y., Zhao J., Zhou S. Light-Activated ROS-Responsive Nanoplatform Codelivering Apatinib and Doxorubicin for Enhanced Chemo-Photodynamic Therapy of Multidrug-Resistant Tumors. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces. 2018;10(21):17672–17684. doi: 10.1021/acsami.8b04163. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

