Kinetic and modeling data on phenol removal by Iron-modified Scoria Powder (FSP) from aqueous solutions
- PMID: 30225308
- PMCID: PMC6138982
- DOI: 10.1016/j.dib.2018.08.068
Kinetic and modeling data on phenol removal by Iron-modified Scoria Powder (FSP) from aqueous solutions
Abstract
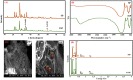
Phenol present in industrial effluents is a toxicant matter which causes pollution of environments aqueous. In this work, scoria was modified by iron in order to increasing of adsorbent efficiency and effective removing of phenol. Effects of independent variables including pH, adsorbents dosage, contact time and adsorbate concentration on removing of phenol were studied by response surface methodology (RSM) based on the central composite designs (CCD). The characterization of raw scoria powder (RSP) and Iron-modified Scoria Powder (FSP) was determined via Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and Energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDS). The obtained data showed modification by iron caused the growth of new crystalline of iron oxide on the surface of FSP. Evaluated data by RSM indicated the all variables especially pH are effective in removing of phenol (P-value < 0.001) and optimum condition was obtained at pH = 5, phenol concentration = 50 mg/l, adsorbent dosage = 1 g/l and contact time = 100 min to the value of 94.99% with desirability of 0.939. Results revealed that data were fitted by Langmuir isotherm (R2 = 0.9938) and pseudo second order kinetic (R2 = 0.9976). It was found that iron causes increasing the site active of scoria and let to significant removal of phenol.
Keywords: Aqueous environment; Iron-Modified scoria; Phenol; RSM.
Figures



References
-
- Federation W.E. American Public Health Association (APHA); Washington, DC, USA: 2005. American Public Health Association. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater.
-
- Karimaei M., Sharafi K., Moradi M., Ghaffari H.R., Biglari H., Arfaeinia H., Fattahi N. Optimization of a methodology for simultaneous determination of twelve chlorophenols in environmental water samples using in situ derivatization and continuous sample drop flow microextraction combined with gas chromatography-electron-capture detection. Anal. Methods. 2017;9:2865–2872.
-
- Moradi M., Mansouri A.M., Azizi N., Amini J., Karimi K., Sharafi K. Adsorptive removal of phenol from aqueous solutions by copper (Cu)-modified scoria powder: process modeling and kinetic evaluation. Desalin. Water Treat. 2016;57:11820–11834.
-
- Biglari H., Afsharnia M., Alipour V., Khosravi R., Sharafi K., Mahvi A.H. A review and investigation of the effect of nanophotocatalytic ozonation process for phenolic compound removal from real effluent of pulp and paper industry. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017;24:4105–4116. - PubMed
-
- Moradi M., Fazlzadehdavil M., Pirsaheb M., Mansouri Y., Khosravi T., Sharafi K. Response surface methodology (RSM) and its application for optimization of ammonium ions removal from aqueous solutions by pumice as a natural and low cost adsorbent. Arch. Environ. Prot. 2016;42:33–43.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

