The fecal virome of red-crowned cranes
- PMID: 30225519
- PMCID: PMC7086969
- DOI: 10.1007/s00705-018-4037-x
The fecal virome of red-crowned cranes
Abstract
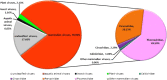
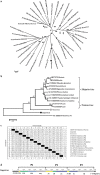
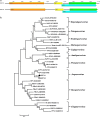
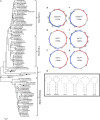
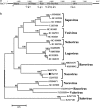
The red-crowned crane is one of the rarest crane species, and its population is decreasing due to loss of habitat, poisoning, and infections. Using a viral metagenomics approach, we analyzed the virome of feces from wild and captive red-crowned cranes, which were pooled separately. Vertebrate viruses belonging to the families Picornaviridae, Parvoviridae, Circoviridae, and Caliciviridae were detected. Among the members of the family Picornaviridae, we found three that appear to represent new genera. Six nearly complete genomes from members of the family Parvoviridae were also obtained, including four new members of the proposed genus "Chapparvovirus", and two members of the genus Aveparvovirus. Six small circular DNA genomes were also characterized. One nearly complete genome showing a low level of sequence identity to caliciviruses was also characterized. Numerous viruses believed to infect insects, plants, and crustaceans were also identified, which were probably derived from the diet of red-crowned cranes. This study increases our understanding of the enteric virome of red-crowned cranes and provides a baseline for comparison to those of other birds or following disease outbreaks.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Liu DW, Liu HY, Zhang HB, Cao MC, Sun Y, Wu WD, Lu CH. Potential natural exposure of endangered red-crowned crane (Grus japonensis) to mycotoxins aflatoxin B1, deoxynivalenol, zearalenone, T-2 toxin, and ochratoxin A. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2016;17:158–168. doi: 10.1631/jzus.B1500211. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- No. 2017YFC1200201/National Key Research and Development Programs of China
- No. 81741062/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- No. BE2017693/Jiangsu Provincial Key Research and Development Projects
- No. 12JDG085/the Professional Research Foundation for Advanced Talents of Jiangsu University
- No. 13JDG087/the Professional Research Foundation for Advanced Talents of Jiangsu University
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

