Human Pegivirus in Patients with Encephalitis of Unclear Etiology, Poland
- PMID: 30226156
- PMCID: PMC6154136
- DOI: 10.3201/eid2410.180161
Human Pegivirus in Patients with Encephalitis of Unclear Etiology, Poland
Abstract
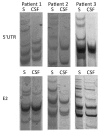
Human pegivirus (HPgV), previously called hepatitis G virus or GB virus C, is a lymphotropic virus with undefined pathology. Because many viruses from the family Flaviviridae, to which HPgV belongs, are neurotropic, we studied whether HPgV could infect the central nervous system. We tested serum and cerebrospinal fluid samples from 96 patients with a diagnosis of encephalitis for a variety of pathogens by molecular methods and serology; we also tested for autoantibodies against neuronal antigens. We found HPgV in serum and cerebrospinal fluid from 3 patients who had encephalitis of unclear origin; that is, all the markers that had been tested were negative. Single-strand confirmation polymorphism and next-generation sequencing analysis revealed differences between the serum and cerebrospinal fluid-derived viral sequences, which is compatible with the presence of a separate HPgV compartment in the central nervous system. It is unclear whether HPgV was directly responsible for encephalitis in these patients.
Keywords: GB virus C; Poland; compartmentalization; encephalitis; hepatitis; human pegivirus; pegivirus; viruses.
Figures



References
-
- Simons JN, Leary TP, Dawson GJ, Pilot-Matias TJ, Muerhoff AS, Schlauder GG, et al. Isolation of novel virus-like sequences associated with human hepatitis. Nat Med. 1995;1:564–9. - PubMed
-
- Linnen J, Wages J Jr, Zhang-Keck ZY, Fry KE, Krawczynski KZ, Alter H, et al. Molecular cloning and disease association of hepatitis G virus: a transfusion-transmissible agent. Science. 1996;271:505–8. - PubMed
-
- Adams MJ, King AM, Carstens EB. Ratification vote on taxonomic proposals to the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses (2013). Arch Virol. 2013;158:2023–30. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

