Experimental evaluation of the importance of colonization history in early-life gut microbiota assembly
- PMID: 30226190
- PMCID: PMC6143339
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.36521
Experimental evaluation of the importance of colonization history in early-life gut microbiota assembly
Abstract
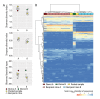
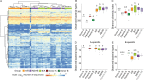
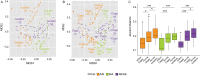
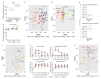
The factors that govern assembly of the gut microbiota are insufficiently understood. Here, we test the hypothesis that inter-individual microbiota variation can arise solely from differences in the order and timing by which the gut is colonized early in life. Experiments in which mice were inoculated in sequence either with two complex seed communities or a cocktail of four bacterial strains and a seed community revealed that colonization order influenced both the outcome of community assembly and the ecological success of individual colonizers. Historical contingency and priority effects also occurred in Rag1-/- mice, suggesting that the adaptive immune system is not a major contributor to these processes. In conclusion, this study established a measurable effect of colonization history on gut microbiota assembly in a model in which host and environmental factors were strictly controlled, illuminating a potential cause for the high levels of unexplained individuality in host-associated microbial communities.
Keywords: Lactobacillus; colonisation history; community ecology; ecology; gut microbiota; historical contingency; mouse; priority effect.
© 2018, Martínez et al.
Conflict of interest statement
IM, MM, JG, HK, HD, RS, PJ, RC, NM, SK, AB, DP, JW No competing interests declared, AR Daniel A. Peterson is affiliated with Eli Lilly & Co.. The author has no financial interests to declare.
Figures






References
-
- Atarashi K, Tanoue T, Shima T, Imaoka A, Kuwahara T, Momose Y, Cheng G, Yamasaki S, Saito T, Ohba Y, Taniguchi T, Takeda K, Hori S, Ivanov II, Umesaki Y, Itoh K, Honda K. Induction of colonic regulatory T cells by indigenous Clostridium species. Science. 2011;331:337–341. doi: 10.1126/science.1198469. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bates D, Maechler M, Bolker B, Walker S. Fitting linear mixed-effects models using lme4. Journal of Statistical Software. 2015;67:1–91. doi: 10.18637/jss.v067.i01. - DOI
-
- Benson AK, Kelly SA, Legge R, Ma F, Low SJ, Kim J, Zhang M, Oh PL, Nehrenberg D, Hua K, Kachman SD, Moriyama EN, Walter J, Peterson DA, Pomp D. Individuality in gut Microbiota composition is a complex polygenic trait shaped by multiple environmental and host genetic factors. PNAS. 2010;107:18933–18938. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1007028107. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

