Contributions of Nociresponsive Area 3a to Normal and Abnormal Somatosensory Perception
- PMID: 30227224
- PMCID: PMC6420406
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jpain.2018.08.009
Contributions of Nociresponsive Area 3a to Normal and Abnormal Somatosensory Perception
Abstract
Traditionally, cytoarchitectonic area 3a of primary somatosensory cortex (SI) has been regarded as a proprioceptive relay to motor cortex. However, neuronal spike-train recordings and optical intrinsic signal imaging, obtained from nonhuman sensorimotor cortex, show that neuronal activity in some of the cortical columns in area 3a can be readily triggered by a C-nociceptor afferent drive. These findings indicate that area 3a is a critical link in cerebral cortical encoding of secondary/slow pain. Also, area 3a contributes to abnormal pain processing in the presence of activity-dependent reversal of gamma-aminobutyric acid A receptor-mediated inhibition. Accordingly, abnormal processing within area 3a may contribute mechanistically to generation of clinical pain conditions. PERSPECTIVE: Optical imaging and neurophysiological mapping of area 3a of SI has revealed substantial driving from unmyelinated cutaneous nociceptors, complementing input to areas 3b and 1 of SI from myelinated nociceptors and non-nociceptors. These and related findings force a reconsideration of mechanisms for SI processing of pain.
Keywords: C-nociception; gamma-aminobutyric acid reversal; pain affect; secondary pain; somatosensory cortex.
Copyright © 2019. Published by Elsevier Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
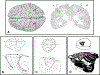
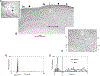
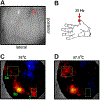
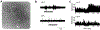




Similar articles
-
A newly identified nociresponsive region in the transitional zone (TZ) in rat sensorimotor cortex.Brain Res. 2019 Aug 15;1717:228-234. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2019.04.028. Epub 2019 Apr 24. Brain Res. 2019. PMID: 31028729 Free PMC article.
-
A nociresponsive specific area of human somatosensory cortex within BA3a: BA3c?Neuroimage. 2020 Nov 1;221:117187. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2020.117187. Epub 2020 Jul 22. Neuroimage. 2020. PMID: 32711068 Free PMC article.
-
Optical imaging of nociception in primary somatosensory cortex of non-human primates.Sheng Li Xue Bao. 2008 Oct 25;60(5):664-8. Sheng Li Xue Bao. 2008. PMID: 18958375
-
Role of primary somatosensory cortex in the coding of pain.Pain. 2013 Mar;154(3):334-344. doi: 10.1016/j.pain.2012.10.021. Epub 2012 Nov 3. Pain. 2013. PMID: 23245864 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Insights Into Spinal Dorsal Horn Circuit Function and Dysfunction Using Optical Approaches.Front Neural Circuits. 2020 Jun 12;14:31. doi: 10.3389/fncir.2020.00031. eCollection 2020. Front Neural Circuits. 2020. PMID: 32595458 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Metabotropic Glutamate Receptor 5 in the Dysgranular Zone of Primary Somatosensory Cortex Mediates Neuropathic Pain in Rats.Biomedicines. 2022 Jul 7;10(7):1633. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10071633. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 35884938 Free PMC article.
-
Focality of the Induced E-Field Is a Contributing Factor in the Choice of TMS Parameters: Evidence from a 3D Computational Model of the Human Brain.Brain Sci. 2020 Dec 18;10(12):1010. doi: 10.3390/brainsci10121010. Brain Sci. 2020. PMID: 33353125 Free PMC article.
-
Cortical activity during the wind-up of flexion reflex and pain: a magnetoencephalographic study using time-frequency analysis.Cereb Cortex. 2023 Jun 8;33(12):7678-7687. doi: 10.1093/cercor/bhad071. Cereb Cortex. 2023. PMID: 36920227 Free PMC article.
-
Arteriovenous malformation presenting as complex regional pain syndrome: illustrative case.J Neurosurg Case Lessons. 2024 Feb 12;7(7):CASE23576. doi: 10.3171/CASE23576. Print 2024 Feb 12. J Neurosurg Case Lessons. 2024. PMID: 38346301 Free PMC article.
-
Disrupted population coding in the prefrontal cortex underlies pain aversion.Cell Rep. 2021 Nov 9;37(6):109978. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2021.109978. Cell Rep. 2021. PMID: 34758316 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aasvang EK, Gmaehle E, Hansen JB, Gmaehle B, Forman JL, Schwarz J, Bittner R, Kehlet H: Predictive risk factors for persistent posthernioectomy pain. Anesthesiol. 112:957–969, 2010 - PubMed
-
- Aderjan D, Stankewitz A, May A: Neuronal mechanisms during repetitive trigemino-nociceptive stimulation in migraine patients. Pain. 151:97–103, 2010 - PubMed
-
- Akbarian S, Grusser OJ, Guldin WO: Thalamic connections of the vestibular cortical fields in the squirrel monkey (Saimiri sciureus). J. Comp. Neurol 326:423–441, 1992 - PubMed
-
- Andreou AP, Goadsby PJ: Topiramate in the treatment of migraine: A kinate (glutamate) receptor antagonist within the trigeminothalamic pathway. Cephalagia. 31: 1343–1358, 2011 - PubMed
-
- Artemenko AR, Kurenkov AL, Filatova SS, Kaube H, Katsarava Z: Effects of topiramate on migraine frequency and cortical excitability in patients with frequent migraine. Cephalagia. 28:203–208, 2008. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

