Genome-Wide Association Studies of 39 Seed Yield-Related Traits in Sesame (Sesamum indicum L.)
- PMID: 30227628
- PMCID: PMC6164633
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms19092794
Genome-Wide Association Studies of 39 Seed Yield-Related Traits in Sesame (Sesamum indicum L.)
Abstract
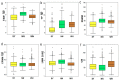
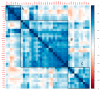
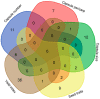
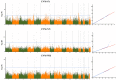
Sesame is poised to become a major oilseed crop owing to its high oil quality and adaptation to various ecological areas. However, the seed yield of sesame is very low and the underlying genetic basis is still elusive. Here, we performed genome-wide association studies of 39 seed yield-related traits categorized into five major trait groups, in three different environments, using 705 diverse lines. Extensive variation was observed for the traits with capsule size, capsule number and seed size-related traits, found to be highly correlated with seed yield indexes. In total, 646 loci were significantly associated with the 39 traits (p < 10-7) and resolved to 547 quantitative trait loci QTLs. We identified six multi-environment QTLs and 76 pleiotropic QTLs associated with two to five different traits. By analyzing the candidate genes for the assayed traits, we retrieved 48 potential genes containing significant functional loci. Several homologs of these candidate genes in Arabidopsis are described to be involved in seed or biomass formation. However, we also identified novel candidate genes, such as SiLPT3 and SiACS8, which may control capsule length and capsule number traits. Altogether, we provided the highly-anticipated basis for research on genetics and functional genomics towards seed yield improvement in sesame.
Keywords: QTL; candidate gene; genome-wide association study; sesame; yield.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, and in the decision to publish the results.
Figures

References
-
- Anilakumar K.R., Pal A., Khanum F., Bawa A.S. Nutritional, medicinal and industrial uses of sesame (Sesamum indicum L.) seeds: An overview. Agric. Conspec. Sci. 2010;75:159–168.
-
- Dossa K., Wei X., Niang M., Liu P., Zhang Y., Wang L., Liao B., Cissé N., Zhang X., Diouf D. Near-infrared reflectance spectroscopy reveals wide variation in major components of sesame seeds from Africa and Asia. Crop J. 2018;6:202–206. doi: 10.1016/j.cj.2017.10.003. - DOI
-
- Ingersent K.A. World agriculture: Towards 2015/2030–An FAO perspective. J. Agric. Econ. 2003;54:513–515.
-
- Langham D.R. Phenology of Sesame. In: Janick J., Whipley A., editors. Issues in New Crops and New Uses. ASHS Press; Alexandria, VA, USA: 2007. p. 39.
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

