Novel Roles of Non-Coding RNAs in Opioid Signaling and Cardioprotection
- PMID: 30227648
- PMCID: PMC6162605
- DOI: 10.3390/ncrna4030022
Novel Roles of Non-Coding RNAs in Opioid Signaling and Cardioprotection
Abstract
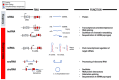
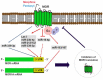
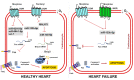
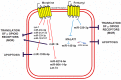
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is a significant cause of morbidity and mortality across the world. A large proportion of CVD deaths are secondary to coronary artery disease (CAD) and myocardial infarction (MI). Even though prevention is the best strategy to reduce risk factors associated with MI, the use of cardioprotective interventions aimed at improving patient outcomes is of great interest. Opioid conditioning has been shown to be effective in reducing myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury (IRI) and cardiomyocyte death. However, the molecular mechanisms behind these effects are under investigation and could provide the basis for the development of novel therapeutic approaches in the treatment of CVD. Non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs), which are functional RNA molecules that do not translate into proteins, are critical modulators of cardiac gene expression during heart development and disease. Moreover, ncRNAs such as microRNAs (miRNAs) and long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) are known to be induced by opioid receptor activation and regulate opioid signaling pathways. Recent advances in experimental and computational tools have accelerated the discovery and functional characterization of ncRNAs. In this study, we review the current understanding of the role of ncRNAs in opioid signaling and opioid-induced cardioprotection.
Keywords: cardioprotection; cardiovascular disease; lncRNA; miRNA; ncRNA; opioids.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Non-coding RNAs as therapeutic targets for preventing myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury.Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2018 Mar;22(3):247-261. doi: 10.1080/14728222.2018.1439015. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2018. PMID: 29417868 Review.
-
Non-Coding RNAs: Prevention, Diagnosis, and Treatment in Myocardial Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Mar 1;23(5):2728. doi: 10.3390/ijms23052728. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35269870 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Non-coding RNAs modulate autophagy in myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury: a systematic review.J Cardiothorac Surg. 2021 May 22;16(1):140. doi: 10.1186/s13019-021-01524-9. J Cardiothorac Surg. 2021. PMID: 34022925 Free PMC article.
-
Deciphering Non-coding RNAs in Cardiovascular Health and Disease.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2018 Jul 2;5:73. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2018.00073. eCollection 2018. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2018. PMID: 30013975 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Impact of Opioids on Epigenetic Modulation in Myocardial Ischemia and Reperfusion Injury: Focus on Non-coding RNAs.J Cardiovasc Transl Res. 2025 Apr 8. doi: 10.1007/s12265-025-10609-y. Online ahead of print. J Cardiovasc Transl Res. 2025. PMID: 40198537 Review.
Cited by
-
Opioids Preconditioning Upon Renal Function and Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury: A Narrative Review.Medicina (Kaunas). 2019 Aug 23;55(9):522. doi: 10.3390/medicina55090522. Medicina (Kaunas). 2019. PMID: 31443610 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Reactive Oxygen Species Related Noncoding RNAs as Regulators of Cardiovascular Diseases.Int J Biol Sci. 2019 Jan 24;15(3):680-687. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.30464. eCollection 2019. Int J Biol Sci. 2019. PMID: 30745854 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Pharmacogenomics-Based In Silico Investigation of Opioid Prescribing in Post-operative Spine Pain Management and Personalized Therapy.Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2024 May 27;44(1):47. doi: 10.1007/s10571-024-01466-5. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2024. PMID: 38801645 Free PMC article.
-
Breast Cancer and Anaesthesia: Genetic Influence.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jul 17;22(14):7653. doi: 10.3390/ijms22147653. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34299272 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pharmacological Conditioning of the Heart: An Update on Experimental Developments and Clinical Implications.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Mar 3;22(5):2519. doi: 10.3390/ijms22052519. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33802308 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

