Structural and Functional Pulmonary Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Pediatrics-From the Neonate to the Young Adult
- PMID: 30228041
- PMCID: PMC6535094
- DOI: 10.1016/j.acra.2018.08.006
Structural and Functional Pulmonary Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Pediatrics-From the Neonate to the Young Adult
Abstract
The clinical imaging modalities available to investigate pediatric pulmonary conditions such as bronchopulmonary dysplasia, cystic fibrosis, and asthma are limited primarily to chest x-ray radiograph and computed tomography. As the challenges that historically limited the application of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to the lung have been overcome, its clinical potential has greatly expanded. In this review article, recent advances in pulmonary MRI including ultrashort echo time and hyperpolarized-gas MRI techniques are discussed with an emphasis on pediatric research and translational applications.
Keywords: MRI; Pediatrics; Pulmonary.
Copyright © 2018 The Association of University Radiologists. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


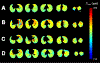
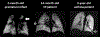
References
-
- Brenner D, Elliston C, Hall E, et al. Estimated risks of radiation-induced fatal cancer from pediatric CT. AJR Am J Roentgenol 2001; 176:289–296. - PubMed
-
- Hatabu H, Alsop DC, Listerud J, et al. T2* and proton density measurement of normal human lung parenchyma using submillisecond echo time gradient echo magnetic resonance imaging. Eur J Radiol 1999; 29: 245–252. - PubMed
-
- Ohno Y, Koyama H, Yoshikawa T, et al. T2* measurements of 3-T MRI with ultrashort TEs: capabilities of pulmonary function assessment and clinical stage classification in smokers. AJR Am J Roentgenol 2011; 197: W279–W285. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

