Cleaner shrimp are a sustainable option to treat parasitic disease in farmed fish
- PMID: 30228312
- PMCID: PMC6143594
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-018-32293-6
Cleaner shrimp are a sustainable option to treat parasitic disease in farmed fish
Abstract
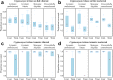
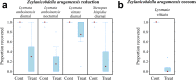
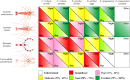
Chemical use is widespread in aquaculture to treat parasitic diseases in farmed fish. Cleaner fish biocontrols are increasingly used in fish farming as an alternative to medicines. However, cleaner fish are susceptible to some of their clients' parasites and their supply is largely dependent on wild harvest. In comparison, cleaner shrimp are not susceptible to fish ectoparasites and they can be reliably bred in captivity. The effectiveness of shrimp in reducing parasites on farmed fish remained unexplored until now. We tested four cleaner shrimp species for their ability to reduce three harmful parasites (a monogenean fluke, a ciliate protozoan, and a leech) on a farmed grouper. All shrimp reduced parasites on fish and most reduced the free-living early-life environmental stages - a function not provided by cleaner fish. Cleaner shrimp are sustainable biocontrol candidates against parasites of farmed fish, with the peppermint cleaner shrimp reducing parasites by up to 98%.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Grunert KG. Sustainability in the food sector: a consumer behaviour perspective. Int. J. Food. Syst. Dynam. 2011;2:207–218.
-
- Banarjee S, Kumar S, Pathak AN. Drug effect on aquaculture and it’s remediation. J. Drug. Delivery. Therap. 2014;4:117–122.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

