Dysphagia
Abstract
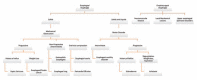
A complaint of dysphagia suggests difficulty in swallowing and is characterized based on the symptoms and location of pathology. Oropharyngeal dysphagia is typically due to difficulty initiating a swallow and is generally due to structural, anatomic or neuromuscular abnormalities. Esophageal dysphagia arises after the swallow and causes include intrinsic structural pathology, extrinsic compression, or disruption in normal motility. Etiologies, methods of evaluation, and management options of dysphagia are reviewed here.
Figures




References
-
- Abdel Jalil AA, Katzka DA, Castell DO. Approach to the patient with dysphagia. Am J Med. 2015;128:1138 e1117–1123. - PubMed
-
- Yamada’s Handbook of Gastroenterology. 3 ed. Wiley-Blackwell; 2013.
-
- Spieker MR. Evaluating dysphagia. Am Fam Physician. 2000;61:3639–3648. - PubMed
-
- Eslick GD, Talley NJ. Dysphagia: epidemiology, risk factors and impact on quality of life--a population-based study. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2008;27:971–979. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
