Recent Breakthroughs and Ongoing Limitations in Cryptosporidium Research
- PMID: 30228873
- PMCID: PMC6124509
- DOI: 10.12688/f1000research.15333.1
Recent Breakthroughs and Ongoing Limitations in Cryptosporidium Research
Abstract
The intestinal apicomplexan parasite Cryptosporidium is a major cause of diarrheal disease in humans worldwide. However, treatment options are severely limited. The search for novel interventions is imperative, yet there are several challenges to drug development, including intractability of the parasite and limited technical tools to study it. This review addresses recent, exciting breakthroughs in this field, including novel cell culture models, strategies for genetic manipulation, transcriptomics, and promising new drug candidates. These advances will stimulate the ongoing quest to understand Cryptosporidium and the pathogenesis of cryptosporidiosis and to develop new approaches to combat this disease.
Keywords: Cryptosporidium; cell culture; drug discovery; genetic modification; transcriptomics.
Conflict of interest statement
No competing interests were disclosed.No competing interests were disclosed.No competing interests were disclosed.No competing interests were disclosed.No competing interests were disclosed.
Figures
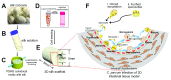


References
-
- Kotloff KL, Blackwelder WC, Nasrin D, et al. : The Global Enteric Multicenter Study (GEMS) of diarrheal disease in infants and young children in developing countries: epidemiologic and clinical methods of the case/control study. Clin Infect Dis. 2012;55 Suppl 4:S232–45. 10.1093/cid/cis753 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

