Analysis of GBE1 mutations via protein expression studies in glycogen storage disease type IV: A report on a non-progressive form with a literature review
- PMID: 30228975
- PMCID: PMC6140619
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ymgmr.2018.09.001
Analysis of GBE1 mutations via protein expression studies in glycogen storage disease type IV: A report on a non-progressive form with a literature review
Abstract
Background: Glycogen storage disease type IV (GSD IV), caused by GBE1 mutations, has a quite wide phenotypic variation. While the classic hepatic form and the perinatal/neonatal neuromuscular forms result in early mortality, milder manifestations include non-progressive form (NP-GSD IV) and adult polyglucosan body disease (APBD). Thus far, only one clinical case of a patient with compound heterozygous mutations has been reported for the molecular analysis of NP-GSD IV. This study aimed to elucidate the molecular basis in a NP-GSD IV patient via protein expression analysis and to obtain a clearer genotype-phenotype relationship in GSD IV.
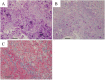
Case presentation: A Japanese boy presented hepatosplenomegaly at 2 years of age. Developmental delay, neurological symptoms, and cardiac dysfunction were not apparent. Observation of hepatocytes with periodic acid-Schiff-positive materials resistant to diastase, coupled with resolution of hepatosplenomegaly at 8 years of age, yielded a diagnosis of NP-GSD IV. Glycogen branching enzyme activity was decreased in erythrocytes. At 13 years of age, he developed epilepsy, which was successfully controlled by carbamazepine.
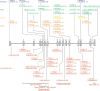
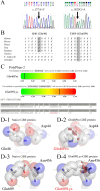
Molecular analysis: In this study, we identified compound heterozygous GBE1 mutations (p.Gln46Pro and p.Glu609Lys). The branching activities of the mutant proteins expressed using E. coli were examined in a reaction with starch. The result showed that both mutants had approximately 50% activity of the wild type protein.
Conclusion: This is the second clinical report of a NP-GSD IV patient with a definite molecular elucidation. Based on the clinical and genotypic overlapping between NP-GSD IV and APBD, we suggest both are in a continuum.
Keywords: APBD, adult polyglucosan body disease; Epilepsy; Functional analysis; GBE, 1,4-alpha-glucan-branching enzyme; GSD; GSD IV, glycogen storage disease type IV; Glycogen storage disease type IV; Glycogenosis, glycogen branching enzyme 1; NP-GSD IV, non-progressive form of glycogen storage disease type IV; RT-PCR, reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction; WT, wild type.
Figures
References
-
- Andersen D.H. Familial cirrhosis of the liver with storage of abnormal glycogen. Lab. Investig. 1956;5:11–20. - PubMed
-
- Magoulas P.L., El-Hattab A.W. In: Glycogen Storage Disease Type IV. Adam M.P., Ardinger H.H., Pagon R.A., Wallace S.E., Bean L.J.H., Stephens K., Amemiya A., editors. GeneReviews®; Seattle (WA): 1993. - PubMed
-
- Moses S.W., Parvari R. The variable presentations of glycogen storage disease type IV: a review of clinical, enzymatic and molecular studies. Curr. Mol. Med. 2002;2:177–188. - PubMed
-
- Bruno C., van Diggelen O.P., Cassandrini D., Gimpelev M., Giuffrè B., Donati M.A., Introvini P., Alegria A., Assereto S., Morandi L., Mora M., Tonoli E., Mascelli S., Traverso M., Pasquini E., Bado M., Vilarinho L., van Noort G., Mosca F., Dimauro S., Zara F., Minetti C. Clinical and genetic heterogeneity of branching enzyme deficiency (glycogenosis type IV) Neurology. 2004;63:1053–1058. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

