A Retrospective Review of a Bed-mounted Projection System for Managing Pediatric Preoperative Anxiety
- PMID: 30229198
- PMCID: PMC6135556
- DOI: 10.1097/pq9.0000000000000087
A Retrospective Review of a Bed-mounted Projection System for Managing Pediatric Preoperative Anxiety
Abstract
Introduction: Most children undergoing anesthesia experience significant preoperative anxiety. We developed a bedside entertainment and relaxation theater (BERT) as an alternative to midazolam for appropriate patients undergoing anesthesia. The primary aim of this study was to determine if BERT was as effective as midazolam in producing cooperative patients at anesthesia induction. Secondary aims reviewed patient emotion and timeliness of BERT utilization.
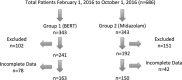
Methods: We conducted a retrospective cohort study of pediatric patients undergoing anesthesia at Lucile Packard Children's Hospital Stanford between February 1, 2016, and October 1, 2016. Logistic regression compared induction cooperation between groups. Multinomial logistic regression compared patients' emotion at induction. Ordinary least squares regression compared preoperative time.
Results: Of the 686 eligible patients, 163 were in the BERT group and 150 in the midazolam. Ninety-three percentage of study patients (290/313) were cooperative at induction, and the BERT group were less likely to be cooperative (P = 0.04). The BERT group was more likely to be "playful" compared with "sedated" (P < 0.001). There was a reduction of 14.7 minutes in preoperative patient readiness associated with BERT (P = 0.001).
Conclusions: Although most patients were cooperative for induction in both groups, the midazolam group was more cooperative. The BERT reduced the preinduction time and was associated with an increase in patients feeling "playful."
Similar articles
-
Varying screen size for passive video distraction during induction of anesthesia in low-risk children: A pilot randomized controlled trial.Paediatr Anaesth. 2019 Jun;29(6):648-655. doi: 10.1111/pan.13636. Epub 2019 Apr 14. Paediatr Anaesth. 2019. PMID: 30916447 Clinical Trial.
-
Use of Bedside Entertainment and Relaxation Theater (BERT) to Reduce Fear and Anxiety Associated With Outpatient Procedures in Pediatric Orthopaedics.J Pediatr Orthop. 2022 Jan 1;42(1):30-34. doi: 10.1097/BPO.0000000000002005. J Pediatr Orthop. 2022. PMID: 34739431 Clinical Trial.
-
A retrospective cohort study of predictors and interventions that influence cooperation with mask induction in children.Paediatr Anaesth. 2020 Aug;30(8):867-873. doi: 10.1111/pan.13930. Epub 2020 Jun 25. Paediatr Anaesth. 2020. PMID: 32452092
-
[Effects of intranasal midazolam premedication on inhaled induction of anesthesia with sevoflurane of pediatric patients].Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2016 Jun 28;96(24):1907-11. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0376-2491.2016.24.007. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2016. PMID: 27373358 Clinical Trial. Chinese.
-
An evidence-based review of parental presence during anesthesia induction and parent/child anxiety.Can J Anaesth. 2009 Jan;56(1):57-70. doi: 10.1007/s12630-008-9008-3. Epub 2008 Dec 20. Can J Anaesth. 2009. PMID: 19247779 Review.
Cited by
-
Management of preoperative anxiety with non-pharmacological methods in pediatric patients in resource-limited settings: a literature review.Ann Med Surg (Lond). 2025 Jan 31;87(2):780-790. doi: 10.1097/MS9.0000000000002912. eCollection 2025 Feb. Ann Med Surg (Lond). 2025. PMID: 40110318 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Kain ZN, Wang SM, Mayes LC, et al. Distress during the induction of anesthesia and postoperative behavioral outcomes. Anesth Analg. 1999;88:1042–1047.. - PubMed
-
- Chorney JM, Kain ZN.Behavioral analysis of children’s response to induction of anesthesia. Anesth Analg. 2009;109:1434–1440.. - PubMed
-
- Wollin SR, Plummer JL, Owen H, et al. Anxiety in children having elective surgery. J Pediatr Nurs. 2004;19:128–132.. - PubMed
-
- Kain ZN, Caldwell-Andrews AA.Preoperative psychological preparation of the child for surgery: an update. Anesthesiol Clin North Am. 2005;23:597–614, vii.. - PubMed
-
- Kain ZN, Caldwell-Andrews AA, Maranets I, et al. Preoperative anxiety and emergence delirium and postoperative maladaptive behaviors. Anesth Analg. 2004;99:1648–1654., table of contents. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources