Progress toward UNAIDS 90-90-90 targets: A respondent-driven survey among female sex workers in Kampala, Uganda
- PMID: 30231030
- PMCID: PMC6145590
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0201352
Progress toward UNAIDS 90-90-90 targets: A respondent-driven survey among female sex workers in Kampala, Uganda
Abstract
Background: We investigated progress towards UNAIDS 90-90-90 targets among female sex workers in Kampala, Uganda, who bear a disproportionate burden of HIV.
Methods: Between April and December 2012, 1,487 female sex workers, defined as women, 15-49 years, residing in greater Kampala, and selling sex for money in the last 6 months, were recruited using respondent-driven sampling. Venous blood was collected for HIV and viral load testing [viral load suppression (VLS) defined as <1,000 copies/mL]. We collected data using audio computer-assisted self-interviews and calculated weighted population-level estimates.
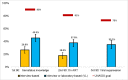
Results: The median age was 27 years (interquartile range: 23 to 32). HIV seroprevalence was 31.4% (95% confidence interval [CI]: 29.0, 33.7%). Among all female sex workers who tested HIV-positive in the survey (population-level targets), 45.5% (95% CI: 40.1, 51.0) had knowledge of their serostatus (population-level target: 90%), 37.8% (95% CI: 32.2, 42.8) self-reported to be on ART (population-level target: 81%), and 35.2% (95% CI: 20.7, 30.4) were virally suppressed (population-level target: 73%).
Conclusions: HIV prevalence among Kampala female sex workers is high, whereas serostatus knowledge and VLS are far below UNAIDS targets. Kampala female sex workers are in need of intensified and targeted HIV prevention and control efforts.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

References
-
- UNAIDS. 90-90-90: an ambitious treatment target to help end the AIDS epidemic. UNAIDS, Geneva, Switzerland: 2014.
-
- Uganda AIDS Commission and UNAIDS. Uganda HIV Modes of Transmission and Prevention Response Analysis. Kampala, Uganda: 2009.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

