Interferons and Proinflammatory Cytokines in Pregnancy and Fetal Development
- PMID: 30231982
- PMCID: PMC6152841
- DOI: 10.1016/j.immuni.2018.07.017
Interferons and Proinflammatory Cytokines in Pregnancy and Fetal Development
Abstract
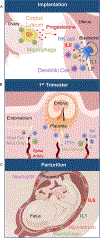
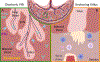
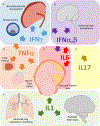
Successful pregnancy requires carefully-coordinated communications between the mother and fetus. Immune cells and cytokine signaling pathways participate as mediators of these communications to promote healthy pregnancy. At the same time, certain infections or inflammatory conditions in pregnant mothers cause severe disease and have detrimental impacts on the developing fetus. In this review, we examine evidence for the role of maternal and fetal immune responses affecting pregnancy and fetal development, both under homeostasis and following infection. We discuss immune responses that are necessary to promote healthy pregnancy and those that lead to congenital disorders and pregnancy complications, with a particular emphasis on the role of interferons and cytokines. Understanding the contributions of the immune system in pregnancy and fetal development provides important insights into the pathogenesis underlying maternal and fetal diseases and sheds insights on possible targets for therapy.
Keywords: autoimmunity; birth defect; congenital diseases; cytokines; infections; innate immunity; interferon; maternal health; placenta.
Copyright © 2018 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Aaltonen R, Heikkinen T, and Hakala K (2005). Transfer of Proinflammatory Cytokines. Obs. Gynecol 106, 802–807. - PubMed
-
- Ahn J, Lee J, and Kim S (2015). Interferon-gamma inhibits the neuronal differentiation of neural progenitor cells by inhibiting the expression of Neurogenin2 via the JAK / STAT1 pathway. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun 466, 52–59. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

