A New Tool to Reveal Bacterial Signaling Mechanisms in Antibiotic Treatment and Resistance
- PMID: 30232125
- PMCID: PMC6283303
- DOI: 10.1074/mcp.RA118.000880
A New Tool to Reveal Bacterial Signaling Mechanisms in Antibiotic Treatment and Resistance
Abstract
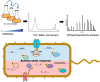
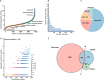
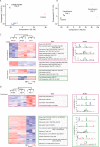
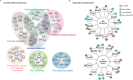
The rapid emergence of antimicrobial resistance is a major threat to human health. Antibiotics modulate a wide range of biological processes in bacteria and as such, the study of bacterial cellular signaling could aid the development of urgently needed new antibiotic agents. Due to the advances in bacterial phosphoproteomics, such a systemwide analysis of bacterial signaling in response to antibiotics has recently become feasible. Here we present a dynamic view of differential protein phosphorylation upon antibiotic treatment and antibiotic resistance. Most strikingly, differential phosphorylation was observed on highly conserved residues of resistance regulating transcription factors, implying a previously unanticipated role of phosphorylation mediated regulation. Using the comprehensive phosphoproteomics data presented here as a resource, future research can now focus on deciphering the precise signaling mechanisms contributing to resistance, eventually leading to alternative strategies to combat antimicrobial resistance.
Keywords: Bacteria; Microbiology; Pathogens; Phosphorylation; Quantification; antimicrobial resistance.
© 2018 Lin et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Antidepressant fluoxetine induces multiple antibiotics resistance in Escherichia coli via ROS-mediated mutagenesis.Environ Int. 2018 Nov;120:421-430. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2018.07.046. Epub 2018 Aug 18. Environ Int. 2018. PMID: 30125859
-
Comparative proteomics to evaluate multi drug resistance in Escherichia coli.Mol Biosyst. 2012 Apr;8(4):1060-7. doi: 10.1039/c1mb05385j. Epub 2011 Nov 28. Mol Biosyst. 2012. PMID: 22120138
-
Detection of acetyltransferase modification of kanamycin, an aminoglycoside antibiotic, in bacteria using ultrahigh-performance liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry.Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom. 2018 Sep 15;32(17):1549-1556. doi: 10.1002/rcm.8160. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom. 2018. PMID: 29781236
-
MarR family proteins are important regulators of clinically relevant antibiotic resistance.Protein Sci. 2020 Mar;29(3):647-653. doi: 10.1002/pro.3769. Epub 2019 Nov 14. Protein Sci. 2020. PMID: 31682303 Free PMC article. Review.
-
After genomics, what proteomics tools could help us understand the antimicrobial resistance of Escherichia coli?J Proteomics. 2012 Jun 6;75(10):2773-89. doi: 10.1016/j.jprot.2011.12.035. Epub 2012 Jan 5. J Proteomics. 2012. PMID: 22245553 Review.
Cited by
-
Clostridioides difficile Phosphoproteomics Shows an Expansion of Phosphorylated Proteins in Stationary Growth Phase.mSphere. 2022 Feb 23;7(1):e0091121. doi: 10.1128/msphere.00911-21. Epub 2022 Jan 5. mSphere. 2022. PMID: 34986318 Free PMC article.
-
A Methanolic Urea-Enhanced Protein Extraction Enabling the Largest Bacterial Phosphorylation Resource.Mol Cell Proteomics. 2025 Jun 24;24(8):101019. doi: 10.1016/j.mcpro.2025.101019. Online ahead of print. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2025. PMID: 40571162 Free PMC article.
-
Fast and Accurate Bacterial Species Identification in Urine Specimens Using LC-MS/MS Mass Spectrometry and Machine Learning.Mol Cell Proteomics. 2019 Dec;18(12):2492-2505. doi: 10.1074/mcp.TIR119.001559. Epub 2019 Oct 4. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2019. PMID: 31585987 Free PMC article.
-
Gene Amplification Uncovers Large Previously Unrecognized Cryptic Antibiotic Resistance Potential in E. coli.Microbiol Spectr. 2021 Dec 22;9(3):e0028921. doi: 10.1128/Spectrum.00289-21. Epub 2021 Nov 10. Microbiol Spectr. 2021. PMID: 34756069 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamic Protein Phosphorylation in Streptococcus pyogenes during Growth, Stationary Phase, and Starvation.Microorganisms. 2024 Mar 20;12(3):621. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms12030621. Microorganisms. 2024. PMID: 38543672 Free PMC article.
References
-
- O'Neill J. (2016) Tackling drug-resistant infections globally: Final report and recommendations https://amr-review.org/sites/default/files/160525_Final%20paper_with%20c...
-
- Hoffman L. R., D'Argenio D. A., MacCoss M. J., Zhang Z., Jones R. A., and Miller S. I. (2005) Aminoglycoside antibiotics induce bacterial biofilm formation. Nature 436, 1171–1175 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

