Deep Sequencing of H7N9 Influenza A Viruses from 16 Infected Patients from 2013 to 2015 in Shanghai Reveals Genetic Diversity and Antigenic Drift
- PMID: 30232169
- PMCID: PMC6147129
- DOI: 10.1128/mSphereDirect.00462-18
Deep Sequencing of H7N9 Influenza A Viruses from 16 Infected Patients from 2013 to 2015 in Shanghai Reveals Genetic Diversity and Antigenic Drift
Abstract
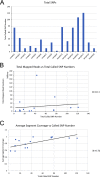
Influenza A virus (IAV) infections are a major public health concern, including annual epidemics, epizootic outbreaks, and pandemics. A significant IAV epizootic outbreak was the H7N9 avian influenza A outbreak in China, which was first detected in 2013 and which has spread over 5 waves from 2013 to 2017, causing human infections in many different Chinese provinces. Here, RNA from primary clinical throat swab samples from 20 H7N9-infected local patients with different clinical outcomes, who were admitted and treated at one hospital in Shanghai, China, from April 2013 to April 2015, was analyzed. Whole-transcriptome amplification, with positive enrichment of IAV RNA, was performed, all 20 samples were subjected to deep sequencing, and data from 16 samples were analyzed in detail. Many single-nucleotide polymorphisms, including ones not previously reported, and many nonsynonymous changes that could affect hemagglutinin head and stalk antibody binding epitopes were observed. Minor populations representing viral quasispecies, including nonsynonymous hemagglutinin changes shared by antigenically variant H7N9 clades identified in the most recent wave of H7N9 infections in 2016 to 2017, were also identified.IMPORTANCE H7N9 subtype avian influenza viruses caused infections in over 1,400 humans from 2013 to 2017 and resulted in almost 600 deaths. It is important to understand how avian influenza viruses infect and cause disease in humans and to assess their potential for efficient person-to-person transmission. In this study, we used deep sequencing of primary clinical material to assess the evolution and potential for human adaptation of H7N9 influenza viruses.
Keywords: DNA sequencing; H7N9; avian viruses.
Copyright © 2018 Xiao et al.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Emergence and Adaptation of a Novel Highly Pathogenic H7N9 Influenza Virus in Birds and Humans from a 2013 Human-Infecting Low-Pathogenic Ancestor.J Virol. 2018 Jan 2;92(2):e00921-17. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00921-17. Print 2018 Jan 15. J Virol. 2018. PMID: 29070694 Free PMC article.
-
Genesis and Spread of Newly Emerged Highly Pathogenic H7N9 Avian Viruses in Mainland China.J Virol. 2017 Nov 14;91(23):e01277-17. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01277-17. Print 2017 Dec 1. J Virol. 2017. PMID: 28956760 Free PMC article.
-
New Threats from H7N9 Influenza Virus: Spread and Evolution of High- and Low-Pathogenicity Variants with High Genomic Diversity in Wave Five.J Virol. 2018 May 14;92(11):e00301-18. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00301-18. Print 2018 Jun 1. J Virol. 2018. PMID: 29563296 Free PMC article.
-
The Effects of Genetic Variation on H7N9 Avian Influenza Virus Pathogenicity.Viruses. 2020 Oct 28;12(11):1220. doi: 10.3390/v12111220. Viruses. 2020. PMID: 33126529 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epidemiology, Evolution, and Pathogenesis of H7N9 Influenza Viruses in Five Epidemic Waves since 2013 in China.Trends Microbiol. 2017 Sep;25(9):713-728. doi: 10.1016/j.tim.2017.06.008. Epub 2017 Jul 19. Trends Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 28734617 Review.
Cited by
-
Deep sequencing of 2009 influenza A/H1N1 virus isolated from volunteer human challenge study participants and natural infections.Virology. 2019 Aug;534:96-107. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2019.06.004. Epub 2019 Jun 13. Virology. 2019. PMID: 31226666 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of Conserved Evolution in H7N9 Avian Influenza Virus Prior Mass Vaccination.Virulence. 2024 Dec;15(1):2395837. doi: 10.1080/21505594.2024.2395837. Epub 2024 Sep 6. Virulence. 2024. PMID: 39240070 Free PMC article.
-
Establishment of a Pig Influenza Challenge Model for Evaluation of Monoclonal Antibody Delivery Platforms.J Immunol. 2020 Aug 1;205(3):648-660. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.2000429. Epub 2020 Jun 26. J Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32591390 Free PMC article.
-
Dose-sparing effect of two adjuvant formulations with a pandemic influenza A/H7N9 vaccine: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 1 clinical trial.PLoS One. 2022 Oct 18;17(10):e0274943. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0274943. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 36256646 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Insights into pathogenesis of fatal COVID-19 pneumonia from histopathology with immunohistochemical and viral RNA studies.Histopathology. 2020 Dec;77(6):915-925. doi: 10.1111/his.14201. Epub 2020 Oct 16. Histopathology. 2020. PMID: 32614086 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Dawood FS, Iuliano AD, Reed C, Meltzer MI, Shay DK, Cheng PY, Bandaranayake D, Breiman RF, Brooks WA, Buchy P, Feikin DR, Fowler KB, Gordon A, Hien NT, Horby P, Huang QS, Katz MA, Krishnan A, Lal R, Montgomery JM, Molbak K, Pebody R, Presanis AM, Razuri H, Steens A, Tinoco YO, Wallinga J, Yu H, Vong S, Bresee J, Widdowson MA. 2012. Estimated global mortality associated with the first 12 months of 2009 pandemic influenza A H1N1 virus circulation: a modelling study. Lancet Infect Dis 12:687–695. doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(12)70121-4. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Gao R, Cao B, Hu Y, Feng Z, Wang D, Hu W, Chen J, Jie Z, Qiu H, Xu K, Xu X, Lu H, Zhu W, Gao Z, Xiang N, Shen Y, He Z, Gu Y, Zhang Z, Yang Y, Zhao X, Zhou L, Li X, Zou S, Zhang Y, Li X, Yang L, Guo J, Dong J, Li Q, Dong L, Zhu Y, Bai T, Wang S, Hao P, Yang W, Zhang Y, Han J, Yu H, Li D, Gao GF, Wu G, Wang Y, Yuan Z, Shu Y. 2013. Human infection with a novel avian-origin influenza A (H7N9) virus. N Engl J Med 368:1888–1897. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1304459. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

