Essential role of IFN-γ in T cell-associated intestinal inflammation
- PMID: 30232288
- PMCID: PMC6237234
- DOI: 10.1172/jci.insight.121886
Essential role of IFN-γ in T cell-associated intestinal inflammation
Abstract
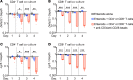
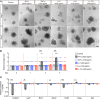
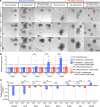
Paneth cells contribute to small intestinal homeostasis by secreting antimicrobial peptides and constituting the intestinal stem cell (ISC) niche. Certain T cell-mediated enteropathies are characterized by extensive Paneth cell depletion coincident with mucosal destruction and dysbiosis. In this study, mechanisms of intestinal crypt injury have been investigated by characterizing responses of mouse intestinal organoids (enteroids) in coculture with mouse T lymphocytes. Activated T cells induced enteroid damage, reduced Paneth cell and Lgr5+ ISC mRNA levels, and induced Paneth cell death through a caspase-3/7-dependent mechanism. IFN-γ mediated these effects, because IFN-γ receptor-null enteroids were unaffected by activated T cells. In mice, administration of IFN-γ induced enteropathy with crypt hyperplasia, villus shortening, Paneth cell depletion, and modified ISC marker expression. IFN-γ exacerbated radiation enteritis, which was ameliorated by treatment with a selective JAK1/2 inhibitor. Thus, IFN-γ induced Paneth cell death and impaired regeneration of small intestinal epithelium in vivo, suggesting that IFN-γ may be a useful target for treating defective mucosal regeneration in enteric inflammation.
Keywords: Cytokines; Gastroenterology; Homeostasis; Inflammation; Inflammatory bowel disease.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures









References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

