Protective effects of Brazilian propolis supplementation on capillary regression in the soleus muscle of hindlimb-unloaded rats
- PMID: 30232713
- PMCID: PMC10717714
- DOI: 10.1007/s12576-018-0639-z
Protective effects of Brazilian propolis supplementation on capillary regression in the soleus muscle of hindlimb-unloaded rats
Abstract
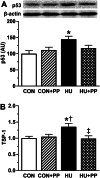
The protective effects of Brazilian propolis on capillary regression induced by chronically neuromuscular inactivity were investigated in rat soleus muscle. Four groups of male Wistar rat were used in this study; control (CON), control plus Brazilian propolis supplementation (CON + PP), 2-week hindlimb unloading (HU), and 2-week hindlimb unloading plus Brazilian propolis supplementation (HU + PP). The rats in the CON + PP and HU + PP groups received two oral doses of 500 mg/kg Brazilian propolis daily (total daily dose 1000 mg/kg) for 2 weeks. Unloading resulted in a decrease in capillary number, luminal diameter, and capillary volume, and an increase in the expression of anti-angiogenic factors, such as p53 and TSP-1, within the soleus muscle. Brazilian propolis supplementation, however, prevented these changes in capillary structure due to unloading through the stimulation of pro-angiogenic factors and suppression of anti-angiogenic factors. These results suggest that Brazilian propolis is a potential non-drug therapeutic agent against capillary regression induced by chronic unloading.
Keywords: Anti-angiogenic factors; Brazilian propolis; Capillary regression; Hindlimb unloading; Muscle atrophy; Oxidative stress.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures






References
-
- de Leon EB, Bortoluzzi A, Rucatti A, Nunes RB, Saur L, Rodrigues M, Oliveira U, Alves-Wagner AB, Xavier LL, Machado UF, Schaan BD, Dall’Ago P. Neuromuscular electrical stimulation improves GLUT-4 and morphological characteristics of skeletal muscle in rats with heart failure. Acta Physiol (Oxf) 2011;201:265–273. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.2010.02176.x. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Kanazashi M, Tanaka M, Murakami S, Kondo H, Nagatomo F, Ishihara A, Roy RR, Fujino H. Amelioration of capillary regression and atrophy of the soleus muscle in hindlimb-unloaded rats by astaxanthin supplementation and intermittent loading. Exp Physiol. 2014;99:1065–1077. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.2014.079988. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- No. 16H07361/Grants-in-Aid for Scientific Research from Japanese Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, science and Technology
- No. 16K12732/Grants-in-Aid for Scientific Research from Japanese Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, science and Technology
- No. 15K16516/Grants-in-Aid for Scientific Research from Japanese Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, science and Technology
- N/A/Yamada Research Grant
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

