Circulating miRNAs as Diagnostic Biomarkers for Parkinson's Disease
- PMID: 30233304
- PMCID: PMC6135037
- DOI: 10.3389/fnins.2018.00625
Circulating miRNAs as Diagnostic Biomarkers for Parkinson's Disease
Abstract
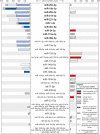
Parkinson's disease (PD) is the second most common neurodegenerative disorder worldwide. Its main neuropathological hallmarks are the degeneration of dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra and alpha-synuclein containing protein inclusions, called Lewy Bodies. The diagnosis of idiopathic PD is still based on the assessment of clinical criteria, leading to an insufficient diagnostic accuracy. Additionally, there is no biomarker available allowing the prediction of the disease course or monitoring the response to therapeutic approaches. So far, protein biomarker candidates such as alpha-synuclein have failed to improve diagnosis of PD. Circulating microRNAs (miRNAs) in body fluids are promising biomarker candidates for PD, as they are easily accessible by non- or minimally-invasive procedures and changes in their expression are associated with pathophysiological processes relevant for PD. Advances in miRNA analysis methods resulted in numerous recent publications on miRNAs as putative biomarkers. Here, we discuss the applicability of different body fluids as sources for miRNA biomarkers, highlight technical aspects of miRNA analysis and give an overview on published studies investigating circulating miRNAs as biomarker candidates for diagnosis of PD and other Parkinsonian syndromes.
Keywords: CSF; Parkinsonian syndromes; Parkinson’s disease; biomarker; blood; miRNA; neurodegeneration.
Figures

References
-
- Burgos K., Malenica I., Metpally R., Courtright A., Rakela B., Beach T., et al. (2014). Profiles of extracellular miRNA in cerebrospinal fluid and serum from patients with Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s diseases correlate with disease status and features of pathology. PLoS One 9:e94839. 10.1371/journal.pone.0094839 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

