RXFP1 Receptor Activation by Relaxin-2 Induces Vascular Relaxation in Mice via a Gαi2-Protein/PI3Kß/γ/Nitric Oxide-Coupled Pathway
- PMID: 30233409
- PMCID: PMC6131674
- DOI: 10.3389/fphys.2018.01234
RXFP1 Receptor Activation by Relaxin-2 Induces Vascular Relaxation in Mice via a Gαi2-Protein/PI3Kß/γ/Nitric Oxide-Coupled Pathway
Abstract
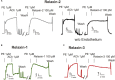
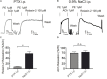
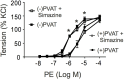
Background: Relaxins are small peptide hormones, which are novel candidate molecules that play important roles in cardiometablic syndrome. Relaxins are structurally related to the insulin hormone superfamily, which provide vasodilatory effects by activation of G-protein-coupled relaxin receptors (RXFPs) and stimulation of endogenous nitric oxide (NO) generation. Recently, relaxin could be demonstrated to activate Gi proteins and phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K) pathways in cultured endothelial cells in vitro. However, the contribution of the Gi-PI3K pathway and their individual components in relaxin-dependent relaxation of intact arteries remains elusive. Methods: We used Gαi2- (Gnai2-/-) and Gαi3-deficient (Gnai3-/-) mice, pharmacological tools and wire myography to study G-protein-coupled signaling pathways involved in relaxation of mouse isolated mesenteric arteries by relaxins. Human relaxin-1, relaxin-2, and relaxin-3 were tested. Results: Relaxin-2 (∼50% relaxation at 10-11 M) was the most potent vasodilatory relaxin in mouse mesenteric arteries, compared to relaxin-1 and relaxin-3. The vasodilatory effects of relaxin-2 were inhibited by removal of the endothelium or treatment of the vessels with N (G)-nitro-L-arginine methyl ester (L-NAME, endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS) inhibitor) or simazine (RXFP1 inhibitor). The vasodilatory effects of relaxin-2 were absent in arteries of mice treated with pertussis toxin (PTX). They were also absent in arteries isolated from Gnai2-/- mice, but not from Gnai3-/- mice. The effects were not affected by FR900359 (Gαq protein inhibitor) or PI-103 (PI3Kα inhibitor), but inhibited by TGX-221 (PI3Kβ inhibitor) or AS-252424 (PI3Kγ inhibitor). Simazine did not influence the anti-contractile effect of perivascular adipose tissue. Conclusion: Our data indicate that relaxin-2 produces endothelium- and NO-dependent relaxation of mouse mesenteric arteries by activation of RXFP1 coupled to Gi2-PI3K-eNOS pathway. Targeting vasodilatory Gi-protein-coupled RXFP1 pathways may provide promising opportunities for drug discovery in endothelial dysfunction and cardiometabolic disease.
Keywords: ADRF; NO; RXFP1 receptor; endothelial Gαi2; perivascular-adipose tissue; relaxin-2; serelaxin.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Localization of relaxin receptors in arteries and veins, and region-specific increases in compliance and bradykinin-mediated relaxation after in vivo serelaxin treatment.FASEB J. 2014 Jan;28(1):275-87. doi: 10.1096/fj.13-233429. Epub 2013 Sep 13. FASEB J. 2014. PMID: 24036884 Free PMC article.
-
Relaxin induces rapid dilation of rodent small renal and human subcutaneous arteries via PI3 kinase and nitric oxide.Endocrinology. 2011 Jul;152(7):2786-96. doi: 10.1210/en.2010-1126. Epub 2011 May 10. Endocrinology. 2011. PMID: 21558316 Free PMC article.
-
G-Protein-coupled receptors as potential drug candidates in preeclampsia: targeting the relaxin/insulin-like family peptide receptor 1 for treatment and prevention.Hum Reprod Update. 2016 Sep;22(5):647-64. doi: 10.1093/humupd/dmw021. Epub 2016 Jul 6. Hum Reprod Update. 2016. PMID: 27385360 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparison of signaling pathways activated by the relaxin family peptide receptors, RXFP1 and RXFP2, using reporter genes.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2007 Jan;320(1):281-90. doi: 10.1124/jpet.106.113225. Epub 2006 Oct 25. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2007. PMID: 17065365
-
'Relaxin' the stiffened heart and arteries: the therapeutic potential for relaxin in the treatment of cardiovascular disease.Pharmacol Ther. 2006 Nov;112(2):529-52. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2005.05.012. Epub 2006 Jul 11. Pharmacol Ther. 2006. PMID: 16814863 Review.
Cited by
-
Minimally invasive, sustained-release relaxin-2 microparticles reverse arthrofibrosis.Sci Transl Med. 2022 Oct 12;14(666):eabo3357. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.abo3357. Epub 2022 Oct 12. Sci Transl Med. 2022. PMID: 36223449 Free PMC article.
-
A human cell atlas of fetal gene expression.Science. 2020 Nov 13;370(6518):eaba7721. doi: 10.1126/science.aba7721. Science. 2020. PMID: 33184181 Free PMC article.
-
Function, Regulation and Biological Roles of PI3Kγ Variants.Biomolecules. 2019 Aug 30;9(9):427. doi: 10.3390/biom9090427. Biomolecules. 2019. PMID: 31480354 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Myogenic Vasoconstriction Requires Canonical Gq/11 Signaling of the Angiotensin II Type 1 Receptor.J Am Heart Assoc. 2022 Feb 15;11(4):e022070. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.121.022070. Epub 2022 Feb 8. J Am Heart Assoc. 2022. PMID: 35132870 Free PMC article.
-
Serelaxin activates eNOS, suppresses inflammation, attenuates developmental delay and improves cognitive functions of neonatal rats after germinal matrix hemorrhage.Sci Rep. 2020 May 15;10(1):8115. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-65144-4. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32415164 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bell R. J., Eddie L. W., Lester A. R., Wood E. C., Johnston P. D., Niall H. D. (1987). Relaxin in human pregnancy serum measured with an homologous radioimmunoassay. Obstet. Gynecol. 69 585–589. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

