Estrogen Therapy Worsens Cardiac Function and Remodeling and Reverses the Effects of Exercise Training After Myocardial Infarction in Ovariectomized Female Rats
- PMID: 30233413
- PMCID: PMC6134041
- DOI: 10.3389/fphys.2018.01242
Estrogen Therapy Worsens Cardiac Function and Remodeling and Reverses the Effects of Exercise Training After Myocardial Infarction in Ovariectomized Female Rats
Abstract
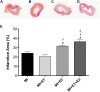
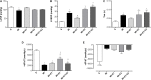
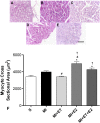
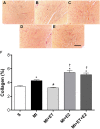
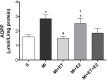
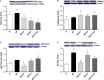
There is an increase in the incidence of cardiovascular events such as myocardial infarction (MI) after menopause. However, the use of estrogen therapy (E2) remains controversial. The aim of this study was to evaluate the effects of E2, alone and combined with exercise training (ET), on cardiac function and remodeling in ovariectomized (OVX) rats after MI. Wistar female rats underwent ovariectomy, followed by MI induction were separated into five groups: S; MI; MI+ET; MI+E2; and MI+ET+E2. Fifteen days after MI or sham surgery, treadmill ET and/or estrogen therapy [17-β estradiol-3-benzoate (E2), s.c. three times/week] were initiated and maintained for 8 weeks. After the treatment and/or training period, the animals underwent cardiac hemodynamic evaluation through catheterization of the left ventricle (LV); the LV systolic and diastolic pressures (LVSP and LVEDP, respectively), maximum LV contraction and relaxation derivatives (dP/dt+ and dP/dt-), and isovolumic relaxation time (Tau) were assessed. Moreover, histological analyses of the heart (collagen and hypertrophy), cardiac oxidative stress [advanced oxidation protein products (AOPPs)], pro- and antioxidant protein expression by Western blotting and antioxidant enzyme activity in the heart were evaluated. The MI reduced the LVSP, dP/dt+ and dP/dt- but increased the LVEDP and Tau. E2 did not prevent the MI-induced changes in cardiac function, even when combined with ET. An increase in the dP/dt+ was observed in the E2 group compared with the MI group. There were no changes in collagen deposition and myocyte hypertrophy caused by the treatments. The increases in AOPP, gp91-phox, and angiotensin II type 1 receptor expression induced by MI were not reduced by E2. There were no changes in the expression of catalase caused by MI or by the treatments, although, a reduction in superoxide dismutase (SOD) expression occurred in the groups subjected to E2 treatment. Whereas there were post-MI reductions in activities of SOD and catalase enzymes, only that of SOD was prevented by ET. Therefore, we conclude that E2 therapy does not prevent the MI-induced changes in cardiac function and worsens parameters related to cardiac remodeling. Moreover, E2 reverses the positive effects of ET when used in combination, in OVX infarcted female rats.
Keywords: cardiac function; estrogen therapy; ovariectomy; oxidative stress; remodeling.
Figures
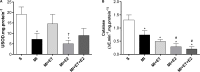
Similar articles
-
Exercise training reduces cardiac dysfunction and remodeling in ovariectomized rats submitted to myocardial infarction.PLoS One. 2014 Dec 31;9(12):e115970. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0115970. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25551214 Free PMC article.
-
The ACE 2 activator diminazene aceturate (DIZE) improves left ventricular diastolic dysfunction following myocardial infarction in rats.Biomed Pharmacother. 2018 Nov;107:212-218. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2018.07.170. Epub 2018 Aug 6. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018. PMID: 30092400
-
Diet with isolated soy protein reduces oxidative stress and preserves ventricular function in rats with myocardial infarction.Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 2009 Feb;19(2):91-7. doi: 10.1016/j.numecd.2008.03.001. Epub 2008 Jun 19. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 2009. PMID: 18571392
-
Clinical aspects of left ventricular diastolic function assessed by Doppler echocardiography following acute myocardial infarction.Dan Med Bull. 2001 Nov;48(4):199-210. Dan Med Bull. 2001. PMID: 11767125 Review.
-
Cardiac remodeling and physical training post myocardial infarction.World J Cardiol. 2015 Feb 26;7(2):52-64. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v7.i2.52. World J Cardiol. 2015. PMID: 25717353 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Effects of Late Aerobic Exercise on Cardiac Remodeling of Rats with Small-Sized Myocardial Infarction.Arq Bras Cardiol. 2021 Apr;116(4):784-792. doi: 10.36660/abc.20190813. Arq Bras Cardiol. 2021. PMID: 33886729 Free PMC article. English, Portuguese.
-
Effects and Safety of Sacubitril/Valsartan for Patients with Myocardial Infarction: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.J Healthc Eng. 2022 Jan 5;2022:7840852. doi: 10.1155/2022/7840852. eCollection 2022. J Healthc Eng. 2022. Retraction in: J Healthc Eng. 2023 Dec 6;2023:9791273. doi: 10.1155/2023/9791273. PMID: 35035857 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Protective Effects of Estrogen on Cardiovascular Disease Mediated by Oxidative Stress.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021 Jun 28;2021:5523516. doi: 10.1155/2021/5523516. eCollection 2021. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021. PMID: 34257804 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of β-Adrenergic Receptors and Estrogen in Cardiac Repair after Myocardial Infarction: An Overview.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Aug 19;22(16):8957. doi: 10.3390/ijms22168957. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34445662 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sex-Specific Impact of 17β-Estradiol and Testosterone Levels on Inflammation and Injury in Acute Myocardial Infarction-Preliminary Results.Biomedicines. 2025 Jun 13;13(6):1466. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines13061466. Biomedicines. 2025. PMID: 40564184 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

