Combined effects of Lenvatinib and iodine-131 on cell apoptosis in nasopharyngeal carcinoma through inducing endoplasmic reticulum stress
- PMID: 30233679
- PMCID: PMC6143866
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2018.6652
Combined effects of Lenvatinib and iodine-131 on cell apoptosis in nasopharyngeal carcinoma through inducing endoplasmic reticulum stress
Abstract
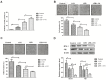
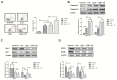
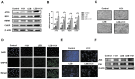
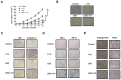
Nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC) is a type of malignant tumor characterized by high invasiveness, metastatic potential and worldwide incidence among patients with head and neck cancer. It has previously been demonstrated that Lenvatinib (LEB) is an efficient anti-cancer agent by multi-targeting of tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Iodine-131 (I-131) therapy has been accepted for the treatment of thyroid cancer and other carcinomas. In the present study, the combined effects of LEB and I-131 were investigated on NPC and the potential signal pathway mediated by LEB and I-131 on NPC cells was explored. Inhibitory effects of LEB and I-131 for NPC cells growth were investigated via MTT assay. Migration and invasion of NPC cells was studied by aggression assays following incubation of LEB and I-131. Apoptosis of NPC cells and tissues were analyzed via flow cytometry and TUNEL assay, respectively. Apoptosis-related gene expression levels in NPC cells following treatment with LEB and I-131 were determined by western blotting. Endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress in NPC cells were analyzed in NPC cells and tumor tissues. Immunohistochemistry was used to analyze the efficacy of LEB and I-131 in NPC-tumor bearing mice. The results demonstrated that combined treatment of LEB and I-131 significantly inhibited growth, apoptosis, migration and invasion of NPC cells compared with single agent therapy. Apoptosis-related gene expression levels of caspase-3 and caspase-9 were upregulated by LEB and I-131, whereas B call lymphoma-2, and P53 were downregulated in NPC cells and tumor tissues. In addition, signal mechanism analysis demonstrated that combined treatment of LEB and I-131 promoted expression levels of activating transcription factor 6, inositol-requiring protein 1 (IER1), protein kinase RNA-like endoplasmic reticulum kinase (RERK), and C/EBP homologous protein in NPC cells. Furthermore, combined treatment of LEB and I-131 markedly inhibited in vivo growth of NPC and further prolonged survival of experimental mice compared with single agent and control groups. Immunohistochemistry indicated that c-jun N-terminal kinase and Caspase-3 were increased in NPS tumor tissues in xenograft models treated with LEB and I-131. Apoptotic bodies were also increased in tumors treated by LEB and I-131. In conclusion, these findings indicate that combined treatment of LEB and I-131 may inhibit NPC growth and aggression through upregulation of ER stress, suggesting combined treatment of LEB and I-131 may be a potential therapeutic schedule for the treatment of NPC.
Keywords: Lenvatinib; apoptosis; endoplasmic reticulum stress; iodine-131; nasopharyngeal carcinoma.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Tetrandrine Induces Apoptosis of Human Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma NPC-TW 076 Cells through Reactive Oxygen Species Accompanied by an Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress Signaling Pathway.Molecules. 2016 Oct 12;21(10):1353. doi: 10.3390/molecules21101353. Molecules. 2016. PMID: 27754332 Free PMC article.
-
Tetrandrine Induces Apoptosis in Human Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma NPC-TW 039 Cells by Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress and Ca2+/Calpain Pathways.Anticancer Res. 2017 Nov;37(11):6107-6118. doi: 10.21873/anticanres.12059. Anticancer Res. 2017. PMID: 29061791
-
A novel curcuminoid exhibits enhanced antitumor activity in nasopharyngeal carcinoma.Int J Oncol. 2016 May;48(5):2175-83. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2016.3425. Epub 2016 Mar 7. Int J Oncol. 2016. PMID: 26983360
-
Taurine exhibits an apoptosis-inducing effect on human nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells through PTEN/Akt pathways in vitro.Amino Acids. 2018 Dec;50(12):1749-1758. doi: 10.1007/s00726-018-2651-2. Epub 2018 Sep 17. Amino Acids. 2018. PMID: 30225664
-
IMB-6G induces endoplasmic reticulum stress-mediated apoptosis in human nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells.Exp Ther Med. 2018 Nov;16(5):4187-4192. doi: 10.3892/etm.2018.6724. Epub 2018 Sep 11. Exp Ther Med. 2018. PMID: 30402159 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
MT1JP-mediated miR-24-3p/BCL2L2 axis promotes Lenvatinib resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma cells by inhibiting apoptosis.Cell Oncol (Dordr). 2021 Aug;44(4):821-834. doi: 10.1007/s13402-021-00605-0. Epub 2021 May 11. Cell Oncol (Dordr). 2021. PMID: 33974236 Free PMC article.
-
Lenvatinib induces anticancer activity in gallbladder cancer by targeting AKT.J Cancer. 2021 Apr 24;12(12):3548-3557. doi: 10.7150/jca.50292. eCollection 2021. J Cancer. 2021. PMID: 33995632 Free PMC article.
-
Advances in targeted therapy mainly based on signal pathways for nasopharyngeal carcinoma.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2020 Oct 23;5(1):245. doi: 10.1038/s41392-020-00340-2. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2020. PMID: 33093441 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cell Proliferation and Apoptosis-Related Genes Affect the Development of Human Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma Through PI3K/AKT Signaling Pathway.Mol Biotechnol. 2021 Nov;63(11):1081-1091. doi: 10.1007/s12033-021-00357-0. Epub 2021 Jul 8. Mol Biotechnol. 2021. PMID: 34236626
References
-
- Ceballos Saenz C, Argyris PP, Manivel JC, Urias Barreras CM, Koutlas IG. Nasopharyngeal hyalinizing clear cell carcinoma: Report of the histopathologic features of a case showing EWSR1 rearrangements by FISH and literature review. Int J Surg Pathol. 2014;22:667–672. doi: 10.1177/1066896914526778. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
