Downregulated caveolin-1 expression serves a potential role in coronary artery spasm by inducing nitric oxide production in vitro
- PMID: 30233709
- PMCID: PMC6143842
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2018.6646
Downregulated caveolin-1 expression serves a potential role in coronary artery spasm by inducing nitric oxide production in vitro
Erratum in
-
Erratum: [Corrigendum] Downregulated caveolin‑1 expression serves a potential role in coronary artery spasm by inducing nitric oxide production in vitro.Exp Ther Med. 2024 Apr 10;27(6):247. doi: 10.3892/etm.2024.12535. eCollection 2024 Jun. Exp Ther Med. 2024. PMID: 38660522 Free PMC article.
Abstract
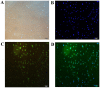
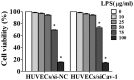
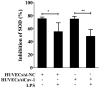
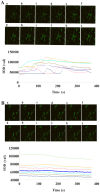
The present study aimed to investigate the effects of downregulated caveolin-1 (Cav-1) expression on nitric oxide (NO) production in lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-damaged primary human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) in a model of coronary artery spasm (CAS) microenvironment induced by acetylcholine (ACh) treatment. Small interfering RNA (siRNA)-mediated Cav-1 downregulation in HUVECs was confirmed by western blotting. The cell viability and superoxide dismutase (SOD) inhibition in HUVECs incubated with LPS (0, 10, 25, 50, 75 and 100 µg/ml) were measured by cell counting kit-8 assay and a SOD kit, respectively. Intracellular Ca2+ [(Ca2+)i] in Fluo4-acetoxymethyl ester-loaded cells was detected by fluorescence microscopy. NO levels in the cell culture supernatants were measured by the nitrate reductase method. The results indicated that transfection with Cav-1 siRNA, in particular siCav-1 (2), downregulated the Cav-1 protein expression. LPS at a dose of 75 µg/ml induced a significant decrease in HUVECs/si-NC and HUVECs/siCav-1 viability compared with the other concentrations of LPS. Compared with the effects of untreated cells, SOD inhibition in HUVECs/si-NC and HUVECs/siCav-1 was significantly decreased by LPS (75 µg/ml). In addition, ACh stimulation caused a greater increase in [Ca2+]i in HUVECs/si-NC as compared with LPS-treated HUVECs/si-NC. ACh stimulation also induced significantly higher NO levels in LPS-treated HUVECs/siCav-1 compared with LPS-treated HUVECs/si-NC cells (P<0.05). In conclusion, the downregulated Cav-1 expression served a key role in NO production in the in vitro model of CAS induced by ACh stimulation of LPS-damaged HUVECs.
Keywords: acetylcholine; caveolin-1; coronary artery spasm; lipopolysaccharide; nitric oxide.
Figures


Similar articles
-
TLR4-Myd88 pathway upregulated caveolin-1 expression contributes to coronary artery spasm.Vascul Pharmacol. 2022 Feb;142:106947. doi: 10.1016/j.vph.2021.106947. Epub 2021 Nov 23. Vascul Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 34822994
-
Effect of lncRNA SNHG15 on LPS-induced vascular endothelial cell apoptosis, inflammatory factor expression and oxidative stress by targeting miR-362-3p.Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand). 2022 Feb 27;67(6):220-227. doi: 10.14715/cmb/2021.67.6.29. Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand). 2022. PMID: 35818193
-
Acetylcholine suppresses LPS-induced endothelial cell activation by inhibiting the MAPK and NF-κB pathways.Eur Cytokine Netw. 2022 Dec 1;33(4):79-89. doi: 10.1684/ecn.2023.0481. Eur Cytokine Netw. 2022. PMID: 37227141
-
[Protective effects of soybean isoflavone on human umbilical vein endothelial cell injury induced by H₂O₂ and lipopolysaccharide].Zhonghua Xin Xue Guan Bing Za Zhi. 2014 Feb;42(2):150-5. Zhonghua Xin Xue Guan Bing Za Zhi. 2014. PMID: 24735628 Chinese.
-
[Extracellular Ca(2+)-sensing receptor-induced extracellular Ca2+ influx is down-regulated by caveolin-1 in human umbilical vein endothelial cells].Sheng Li Xue Bao. 2011 Feb 25;63(1):39-47. Sheng Li Xue Bao. 2011. PMID: 21340433 Chinese.
Cited by
-
Pathophysiological Role of Caveolae in Hypertension.Front Med (Lausanne). 2019 Jul 10;6:153. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2019.00153. eCollection 2019. Front Med (Lausanne). 2019. PMID: 31355199 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Takagi Y, Yasuda S, Takahashi J, Tsunoda R, Ogata Y, Seki A, Sumiyoshi T, Matsui M, Goto T, Tanabe Y, et al. Clinical implications of provocation tests for coronary artery spasm: Safety, arrhythmic complications and prognostic impact: Multicentre registry study of the Japanese coronary spasm association. Eur Heart J. 2013;34:258–267. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehs199. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
