Effects of atrial fibrillation on complications and prognosis of patients receiving emergency PCI after acute myocardial infarction
- PMID: 30233710
- PMCID: PMC6143848
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2018.6640
Effects of atrial fibrillation on complications and prognosis of patients receiving emergency PCI after acute myocardial infarction
Abstract
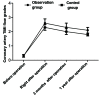
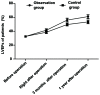
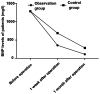
The effects of atrial fibrillation on complications and prognosis of patients receiving emergency percutaneous coronary intervention after acute myocardial infarction (AMI) were investigated. Eighty AMI patients treated with interventional vascular recanalization in the Affiliated Hospital of Weifang Medical University (Weifang, China) from July 2015 to October 2016 were selected, including 40 patients complicated with atrial fibrillation before operation (control group) and 40 patients without atrial fibrillation before operation (observation group). The systolic blood pressure, diastolic blood pressure, heart rate, arrhythmia and common complications after MI were compared. Changes in the coronary artery thrombolysis in myocardial infarction (TIMI) flow grade and left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) of patients were also recorded. Moreover, changes in brain natriuretic peptide (BNP) levels were compared. The recovery time of myocardial enzyme and total troponin in both groups was recorded. The systolic and diastolic blood pressure in the observation group were significantly higher than those in the control group (p<0.05). During the intervention, the total proportion of patients with ventricular arrhythmia, atrial arrhythmia, atrioventricular block and sinus tachycardia in the observation group was significantly lower than that in the control group (p<0.05). The total proportion of common complications after MI in the observation group was obviously lower than that in the control group (p<0.05). Coronary artery TIMI flow grades and LVEFs in the observation group were obviously higher than those in the control group. BNP levels in the observation group were significantly lower than those in the control group. The recovery time of myocardial enzyme and total troponin in the observation group was significantly earlier than that in the control group. Atrial fibrillation has a certain negative effect on the circulatory function in patients with AMI after the interventional therapy, and the proportions of arrhythmia and complications in patients after MI are increased at the same time, so the postoperative recovery of patients is slow with many complications.
Keywords: acute myocardial infarction; atrial fibrillation; complications; percutaneous coronary intervention.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Effects of Tongxinluo Capsule on Platelet Activating Factor, Vascular Endothelial Function, Blood Flow of Thrombolysis in Myocardial Infarction in Acute Myocardial Infarction Patients after Delayed Percutaneous Coronary Intervention].Zhongguo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi. 2016 Apr;36(4):415-20. Zhongguo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi. 2016. PMID: 27323611 Clinical Trial. Chinese.
-
[Risk factors and prognoses analysis of new-onset atrial fibrillation in patients with acute myocardial infarction].Zhonghua Nei Ke Za Zhi. 2019 Feb 1;58(2):133-138. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0578-1426.2019.02.010. Zhonghua Nei Ke Za Zhi. 2019. PMID: 30704200 Chinese.
-
Thrombus aspiration catheter improve the myocardial reperfusion of STEMI patients with high thrombus load during the emergency PCI operation.J Cardiothorac Surg. 2019 Sep 23;14(1):172. doi: 10.1186/s13019-019-0974-z. J Cardiothorac Surg. 2019. PMID: 31547844 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Clinical features and prognosis of acute myocardial infarction caused by non-tumor origin coronary artery embolism.Am J Emerg Med. 2020 Jun;38(6):1185-1191. doi: 10.1016/j.ajem.2020.03.043. Epub 2020 Mar 24. Am J Emerg Med. 2020. PMID: 32229223
-
The effect of nicorandil in patients with acute myocardial infarction undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Ir J Med Sci. 2020 Feb;189(1):119-131. doi: 10.1007/s11845-019-02034-3. Epub 2019 May 30. Ir J Med Sci. 2020. PMID: 31147987
Cited by
-
Establishment and validation of a clinical nomogram model based on serum YKL-40 to predict major adverse cardiovascular events during hospitalization in patients with acute ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction.Front Med (Lausanne). 2023 May 22;10:1158005. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2023.1158005. eCollection 2023. Front Med (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 37283624 Free PMC article.
-
Possible implication of miR-142-3p in coronary microembolization induced myocardial injury via ATXN1L/HDAC3/NOL3 axis.J Mol Med (Berl). 2022 May;100(5):763-780. doi: 10.1007/s00109-022-02198-z. Epub 2022 Apr 12. J Mol Med (Berl). 2022. PMID: 35414011
-
Granulocyte colony-stimulating factor attenuates myocardial remodeling and ventricular arrhythmia susceptibility via the JAK2-STAT3 pathway in a rabbit model of coronary microembolization.BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2020 Feb 17;20(1):85. doi: 10.1186/s12872-020-01385-5. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2020. PMID: 32066388 Free PMC article.
-
Hypertension and Atrial Fibrillation: Bridging the Gap Between Mechanisms, Risk, and Therapy.Medicina (Kaunas). 2025 Feb 19;61(2):362. doi: 10.3390/medicina61020362. Medicina (Kaunas). 2025. PMID: 40005478 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Establishment and application of an intraoperative reperfusion arrhythmia prediction model for PCI in elderly patients with acute coronary syndrome.Am J Transl Res. 2024 Nov 15;16(11):6447-6456. doi: 10.62347/JMBY1770. eCollection 2024. Am J Transl Res. 2024. PMID: 39678573 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Batra G, Friberg L, Erlinge D, James S, Jernberg T, Svennblad B, Wallentin L, Oldgren J. Antithrombotic therapy after myocardial infarction in patients with atrial fibrillation undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention. Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Pharmacother. 2018;6:36–45. doi: 10.1093/ehjcvp/pvx033. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Chen J, Wang LY, Deng C, Jiang XH, Chen TG. The safety and efficacy of oral anticoagulants with dual versus single antiplatelet therapy in patients after percutaneous coronary intervention: A meta-analysis. Medicine (Baltimore) 2017;96:e8015. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000008015. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000008015. - DOI - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cannon CP, Bhatt DL, Oldgren J, Lip GYH, Ellis SG, Kimura T, Maeng M, Merkely B, Zeymer U, Gropper S, et al. RE-DUAL PCI Steering Committee and Investigators: Dual antithrombotic therapy with dabigatran after PCI in atrial fibrillation. N Engl J Med. 2017;377:1513–1524. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1708454. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Hwang KK, Eom SY, Lee SY, Kim SM, Cho MC, Kim YJ, Seung KB, Jeong MH, Bae JW, other Korea Acute Myocardial Infarction Registry Investigators Atrial fibrillation on admission is related with higher mortality in ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction patients. Int Heart J. 2017;58:486–494. doi: 10.1536/ihj.16-286. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
