Reduced expression of microRNA-199a-3p is associated with vascular endothelial cell injury induced by type 2 diabetes mellitus
- PMID: 30233719
- PMCID: PMC6143878
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2018.6655
Reduced expression of microRNA-199a-3p is associated with vascular endothelial cell injury induced by type 2 diabetes mellitus
Abstract
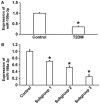
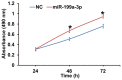
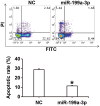
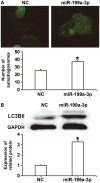
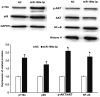
The aim of the present study was to investigate the function and mechanism of action of microRNA (miRNA or miR)-199a-3p in vascular endothelial cell injury induced by type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). A total of 36 patients with T2DM (26 males and 10 females; mean age, 52.5±7.0 years) and 20 healthy subjects (10 males and 10 females; mean age, 55.6±4.5 years) were included in the present study. Peripheral blood samples were obtained from all participants and total RNA was extracted Reverse transcription-quantitative polymerase chain reaction was performed to determine the expression of miR-199a-3p. Following the transfection of human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) with a negative control (NC) miRNA or miR-199a-3p mimics, cell proliferation was assessed using a Cell Counting kit-8 assay. Cell migration was investigated using Transwell assays and flow cytometry was performed to detect the apoptosis of HUVECs. HUVECs were infected with Ad-GFP-LC3B and laser-scanning confocal microscopy was performed to observe autophagosomes in HUVECs. Western blotting was used to measure the expression of proteins associated with autophagy and the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)/protein kinase B (AKT)/nuclear factor (NF)-κB signaling pathway. MiR-199a-3p was downregulated in peripheral blood from patients with T2DM compared with healthy subjects. Transfection with miR-199a-3p mimics promoted the proliferation and migration of HUVECs. However, miR-199a-3p overexpression inhibited the apoptosis of HUVECs. MiR-199a-3p facilitated HUVEC autophagy by affecting autophagy-associated signaling pathways. Furthermore, miR-199a-3p regulated the biological functions of HUVECs via the PI3K/AKT/NF-κB signaling pathway. The results of the present study suggest that miR-199a-3p expression was reduced in patients with T2DM compared with healthy subjects and may be associated with vascular endothelial cell injury. In addition, miR-199a-3p promoted the proliferation, migration and autophagy of HUVECs, potentially by regulating the PI3K/AKT/NF-κB signaling pathway. Therefore, miR-199a-3p may function as protector of vascular endothelia.
Keywords: microRNA-199a-3p; type 2 diabetes mellitus; vascular endothelial cell injury.
Figures

Similar articles
-
MicroRNA-199a-5p aggravates primary hypertension by damaging vascular endothelial cells through inhibition of autophagy and promotion of apoptosis.Exp Ther Med. 2018 Aug;16(2):595-602. doi: 10.3892/etm.2018.6252. Epub 2018 Jun 6. Exp Ther Med. 2018. PMID: 30116316 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-329-3p alleviates high glucose-induced endothelial cell injury via inhibition of the TLR4/TRAF6/NF-κB signaling pathway.Exp Ther Med. 2021 Jan;21(1):29. doi: 10.3892/etm.2020.9461. Epub 2020 Nov 10. Exp Ther Med. 2021. PMID: 33262815 Free PMC article.
-
Overexpression of microRNA-506-3p aggravates the injury of vascular endothelial cells in patients with hypertension by downregulating Beclin1 expression.Exp Ther Med. 2018 Mar;15(3):2844-2850. doi: 10.3892/etm.2018.5733. Epub 2018 Jan 10. Exp Ther Med. 2018. PMID: 29456688 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-199a-3p inhibits angiogenesis by targeting the VEGF/PI3K/AKT signalling pathway in an in vitro model of diabetic retinopathy.Exp Mol Pathol. 2020 Oct;116:104488. doi: 10.1016/j.yexmp.2020.104488. Epub 2020 Jul 2. Exp Mol Pathol. 2020. PMID: 32622012
-
Overview of microRNA-199a Regulation in Cancer.Cancer Manag Res. 2019 Dec 10;11:10327-10335. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S231971. eCollection 2019. Cancer Manag Res. 2019. PMID: 31849522 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Bta-miR-199a-3p Inhibits LPS-Induced Inflammation in Bovine Mammary Epithelial Cells via the PI3K/AKT/NF-κB Signaling Pathway.Cells. 2022 Nov 7;11(21):3518. doi: 10.3390/cells11213518. Cells. 2022. PMID: 36359915 Free PMC article.
-
An exploration of new methods for metabolic syndrome examination by infrared thermography and knowledge mining.Sci Rep. 2022 Apr 16;12(1):6377. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-10422-6. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35430598 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA expression profiling in tears and blood as predictive biomarkers for anti-VEGF treatment response in wet age-related macular degeneration.Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2024 Sep;262(9):2875-2884. doi: 10.1007/s00417-024-06478-x. Epub 2024 Apr 6. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2024. PMID: 38581435
-
Dysregulation of circulating miRNAs promotes the pathogenesis of diabetes-induced cardiomyopathy.PLoS One. 2021 Apr 28;16(4):e0250773. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0250773. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. Retraction in: PLoS One. 2023 Dec 22;18(12):e0296476. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0296476. PMID: 33909697 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Evaluation of Circulating MicroRNAs and Adipokines in Breast Cancer Survivors with Arm Lymphedema.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Sep 26;23(19):11359. doi: 10.3390/ijms231911359. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36232660 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Iciek R, Brazert M, Wender-Ozegowska E, Pietryga M, Brazert J. Low placental visfatin expression is related to impaired glycaemic control and fetal macrosmia in pregnancies complicated by type 1 diabetes. J Physiol Pharmacol. 2018;69:61–66. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
