Protective role of fentanyl in lipopolysaccharide-induced neuroinflammation in BV-2 cells
- PMID: 30233733
- PMCID: PMC6143851
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2018.6590
Protective role of fentanyl in lipopolysaccharide-induced neuroinflammation in BV-2 cells
Abstract
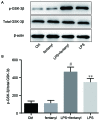
Neurosurgery always results in neuroinflammation, which may activate microglial cells. Previous studies have demonstrated that fentanyl could be used for the induction or maintenance of anesthesia prior to surgery. However, it is unknown if fentanyl attenuates neuroinflammation prophylactically. Cell viability in groups that were treated with different concentrations of fentanyl (0.01, 0.1, 1 or 5 µmol/l) was analyzed by an MTT assay. BV-2 microglial cells were treated with lipopolysaccharide (LPS) at a concentration of 1 µg/ml to mimic neuroinflammation in vitro. BV-2 cells were pretreated with 5 µmol/l fentanyl prior to stimulation by LPS. The protein levels of tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α, interleukin (IL)-1β and IL-10 in the culture medium were assessed by ELISA. The mRNA level of toll-like receptor (TLR)4 was evaluated by reverse transcription-quantitative polymerase chain reaction analysis. The protein levels of TLR4, glycogen synthase kinase (GSK)-3β and phosphorylated (p)-GSK-3β in BV-2 cells were assessed by western blot analysis. The MTT assay demonstrated that low concentrations of fentanyl (0.01, 0.1 or 1 µmol/l) did not affect the cell viability of BV-2 cells, while 5 µmol/l fentanyl significantly reduced BV-2 cell viability. The results of ELISA revealed that LPS significantly upregulated the release of TNF-α, IL-1β and IL-10, which were repressed by fentanyl pretreatment. Fentanyl pretreatment significantly reduced the LPS-induced elevation of TLR4 at mRNA and protein levels as well as p-GSK-3β protein levels in BV-2 cells. In conclusion, fentanyl pretreatment protects BV-2 cells from LPS-induced neuroinflammation by inhibiting TLR4 expression and GSK-3β activation. Neuroinflammation induced by surgery serves an important role in the development of postoperative cognitive dysfunction (POCD) and targeting the TLR4 and GSK-3β signaling pathway may provide a novel therapeutic approach for the treatment of POCD.
Keywords: BV-2 cells; fentanyl; glycogen synthase kinase-3β; neuroinflammation; toll-like receptor 4.
Figures

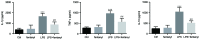


Similar articles
-
Neuroprotective effects of pretreatment with propofol in LPS-induced BV-2 microglia cells: role of TLR4 and GSK-3β.Inflammation. 2012 Oct;35(5):1632-40. doi: 10.1007/s10753-012-9478-x. Inflammation. 2012. PMID: 22588329
-
MicroRNA-181b-5p attenuates early postoperative cognitive dysfunction by suppressing hippocampal neuroinflammation in mice.Cytokine. 2019 Aug;120:41-53. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2019.04.005. Epub 2019 Apr 16. Cytokine. 2019. PMID: 31003188
-
Prophylactic lithium alleviates splenectomy-induced cognitive dysfunction possibly by inhibiting hippocampal TLR4 activation in aged rats.Brain Res Bull. 2015 May;114:31-41. doi: 10.1016/j.brainresbull.2015.02.008. Epub 2015 Apr 1. Brain Res Bull. 2015. PMID: 25839444
-
Dangguishaoyao-San attenuates LPS-induced neuroinflammation via the TLRs/NF-κB signaling pathway.Biomed Pharmacother. 2018 Sep;105:187-194. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2018.05.108. Epub 2018 May 29. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018. PMID: 29857298
-
Semaphorin 3A-Plexin-A1 signaling through ERK activation is crucial for Toll-like receptor-induced NO production in BV-2 microglial cells.Int J Mol Med. 2014 Jun;33(6):1635-42. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2014.1727. Epub 2014 Apr 4. Int J Mol Med. 2014. PMID: 24714875
Cited by
-
Fentanyl dysregulates neuroinflammation and disrupts blood-brain barrier integrity in HIV-1 Tat transgenic mice.J Neurovirol. 2024 Feb;30(1):1-21. doi: 10.1007/s13365-023-01186-4. Epub 2024 Jan 27. J Neurovirol. 2024. PMID: 38280928 Free PMC article.
-
Human Neuronal Cell Lines as An In Vitro Toxicological Tool for the Evaluation of Novel Psychoactive Substances.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jun 24;22(13):6785. doi: 10.3390/ijms22136785. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34202634 Free PMC article.
-
Fentanyl enhances immune cell response through TLR4/MD-2 complex.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Oct 9;15:1468644. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1468644. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39444612 Free PMC article.
-
Chrysomycin A Attenuates Neuroinflammation by Down-Regulating NLRP3/Cleaved Caspase-1 Signaling Pathway in LPS-Stimulated Mice and BV2 Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jun 24;22(13):6799. doi: 10.3390/ijms22136799. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34202695 Free PMC article.
-
Involvement of Anti-Inflammatory and Stress Oxidative Markers in the Antidepressant-like Activity of Aloysia citriodora and Verbascoside on Mice with Bacterial Lipopolysaccharide- (LPS-) Induced Depression.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022 Sep 22;2022:1041656. doi: 10.1155/2022/1041656. eCollection 2022. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022. PMID: 36185078 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
