A case report of acalculous cholecystitis due to Salmonella paratyphi B
- PMID: 30233740
- PMCID: PMC6138858
- DOI: 10.1016/j.radcr.2018.07.013
A case report of acalculous cholecystitis due to Salmonella paratyphi B
Abstract
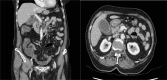
Acute acalculous cholecystitis (AAC) is a rare condition occurring in only 5%-10 % of patients with acute cholecystitis. Systemic illness caused, for example, by E coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Vibrio cholera, and Salmonella species can result acute inflammation of gallbladder wall. It is a surgical emergency and if left untreated can lead to high mortality due to gangrene or perforation of gallbladder. We managed a 60-year-old female with clinical presentation of acute cholecystitis caused by Salmonella-induced gastroenteritis. Prompt use of radiological modalities such as computer tomography (CT scan) and ultrasound played an important role in pathologic diagnosis, overall follow up, and management of the patient.
Keywords: Acalculous cholecystitis; Ischemia; Pericholecystic fluid; Salmonella paratyphi B.
Figures
References
-
- Howard R. Acute acalculous cholecystitis. Am J Surg. 1981;141:194–198. - PubMed
-
- Ryu JK, Ryu KH, Kim KH. Clinical features of acute acalculous cholecystitis. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2003;36:166–169. - PubMed
-
- Barie PS, Fischer E. Acute acalculous cholecystitis. J Am Coll Surg. 1995;180:232–244. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources