Design, Synthesis and Biological Activity Evaluation of S-Substituted 1 H-5-Mercapto-1,2,4-Triazole Derivatives as Antiproliferative Agents in Colorectal Cancer
- PMID: 30234098
- PMCID: PMC6134806
- DOI: 10.3389/fchem.2018.00373
Design, Synthesis and Biological Activity Evaluation of S-Substituted 1 H-5-Mercapto-1,2,4-Triazole Derivatives as Antiproliferative Agents in Colorectal Cancer
Abstract
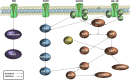
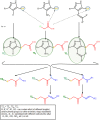
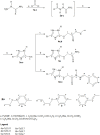
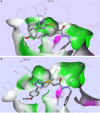
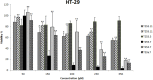
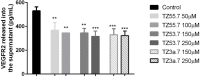
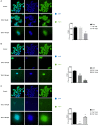
Colon cancer is a widespread pathology with complex biochemical etiology based on a significant number of intracellular signaling pathways that play important roles in carcinogenesis, tumor proliferation and metastasis. These pathways function due to the action of key enzymes that can be used as targets for new anticancer drug development. Herein we report the synthesis and biological antiproliferative evaluation of a series of novel S-substituted 1H-3-R-5-mercapto-1,2,4-triazoles, on a colorectal cancer cell line, HT-29. Synthesized compounds were designed by docking based virtual screening (DBVS) of a previous constructed compound library against protein targets, known for their important role in colorectal cancer signaling: MEK1, ERK2, PDK1, VEGFR2. Among all synthesized structures, TZ55.7, which was retained as a possible PDK1 (phospholipid-dependent kinase 1) inhibitor, exhibited the most significant cytotoxic activity against HT-29 tumor cell line. The same compound alongside other two, TZ53.7 and TZ3a.7, led to a significant cell cycle arrest in both sub G0/G1 and G0/G1 phase. This study provides future perspectives for the development of new agents containing the 1,2,4-mercapto triazole scaffold with antiproliferative activities in colorectal cancer.
Keywords: 1; 2; 4-triazole; antiproliferative; cell cycle; colon cancer; docking.
Figures
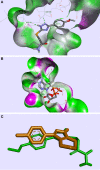

Similar articles
-
Design, Synthesis and Antiproliferative Evaluation of Novel 1,2,4-Triazole/Schiff Base Hybrids with EGFR and B-RAF Inhibitory Activities.Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2019;19(5):697-706. doi: 10.2174/1871520619666181224115346. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2019. PMID: 30582484
-
Study of the Cytotoxic and Bactericidal Effects of Sila-substituted Thioalkyne and Mercapto-thione Compounds based on 1,2,3-Triazole Scaffold.Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 2017 Nov;121(5):390-399. doi: 10.1111/bcpt.12822. Epub 2017 Jul 10. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 2017. PMID: 28613449
-
Exploring the Anticancer Properties of 1,2,3-Triazole-Substituted Andrographolide Derivatives.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025 May 19;18(5):750. doi: 10.3390/ph18050750. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40430567 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis, anticancer activity and molecular modeling studies of 1,2,4-triazole derivatives as EGFR inhibitors.Eur J Med Chem. 2018 Aug 5;156:774-789. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2018.07.024. Epub 2018 Jul 10. Eur J Med Chem. 2018. PMID: 30055463
-
Two decades of the synthesis of mono- and bis-aminomercapto[1,2,4]triazoles.RSC Adv. 2020 Jul 1;10(42):24994-25012. doi: 10.1039/d0ra04208k. eCollection 2020 Jun 29. RSC Adv. 2020. PMID: 35517465 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Antiviral Effect of Polyphenolic Substances in Geranium wilfordii Maxim against HSV-2 Infection Using in vitro and in silico Approaches.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022 May 18;2022:7953728. doi: 10.1155/2022/7953728. eCollection 2022. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022. PMID: 35646147 Free PMC article.
-
New Investigations with Lupane Type A-Ring Azepane Triterpenoids for Antimycobacterial Drug Candidate Design.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Nov 21;22(22):12542. doi: 10.3390/ijms222212542. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34830423 Free PMC article.
-
Unravelling the anticancer potency of 1,2,4-triazole-N-arylamide hybrids through inhibition of STAT3: synthesis and in silico mechanistic studies.Mol Divers. 2021 Feb;25(1):403-420. doi: 10.1007/s11030-020-10131-0. Epub 2020 Aug 23. Mol Divers. 2021. PMID: 32830299
-
Triazoles and Their Derivatives: Chemistry, Synthesis, and Therapeutic Applications.Front Mol Biosci. 2022 Apr 25;9:864286. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2022.864286. eCollection 2022. Front Mol Biosci. 2022. PMID: 35547394 Free PMC article. Review.
-
In Vitro and In Silico Evaluation of Syzygium aromaticum Essential Oil: Effects on Mitochondrial Function and Cytotoxic Potential Against Cancer Cells.Plants (Basel). 2024 Dec 8;13(23):3443. doi: 10.3390/plants13233443. Plants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39683236 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aliabadi A., Mohammadi-Frarni A., Azizi M., Ahmadi F. (2016). Design, synthesis and cytotoxicity evaluation of N-(5-Benzylthio)-4H-1,2,4-Triazol-3-YL)-4-fluorobenzamide derivatives as potential anticancer agents. Pharm. Chem. J. 49, 694–699. 10.1007/s11094-016-1355-8 - DOI
-
- American Cancer Society (2017). Targeted Therapy Drugs for Colorectal Cancer. Available online at: https://www.cancer.org/cancer/colon-rectal-cancer/treating/targeted-ther... (Accessed June 3, 2017).
-
- Araújo R. F., Jr., Lira G. A., Vilac J. A., Guedes H. G., Leitão M. C. A., Lucena H. F., et al. (2015). Pathology – research and practice prognostic and diagnostic implications of MMP-2, MMP-9, and VEGF- α expressions in colorectal cancer. Pathol. Res. Pract. 211, 71–77. 10.1016/j.prp.2014.09.007 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

