A survey of current surgical treatment of early stage breast cancer in China
- PMID: 30234145
- PMCID: PMC6142897
- DOI: 10.18632/oncoscience.445
A survey of current surgical treatment of early stage breast cancer in China
Abstract
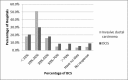
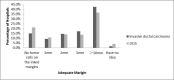
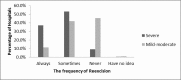
The purpose of this national survey is to explore the patterns of surgical management for early stage breast cancer patients in China. A paper questionnaire survey was sent to the representatives from 520 hospitals who attended an international symposium in Guangzhou, China, 2014. The questionnaire included demographic information, initials and most preferred approaches for breast cancer surgery. The results were presented descriptively. The response rate was 42.5%. Only 7% of hospitals with >50% rate of breast conserving surgery (BCS). Intraoperative frozen sections and additional cavity margins assessment were used at 88% and 30.9% of hospitals, respectively. For invasive carcinoma, 15% of participants defined an adequate margin as no tumor cells on the ink. Sentinel lymph node biopsy (SLNB) was routinely performed in 93.2% of hospitals. Only 16.6% of hospitals would embrace the conclusions of the American College of Surgeons Oncology Group (ACOSOG) Z0011 study and omit axillary lymph node dissection (ALND) for patients who fit the Z0011 criteria. The current patterns for the management of breast cancer patients are still lagging behind. Chinese doctors need to catch up with the updated results of the cutting-edge clinical studies and multiple measures are in need to improve this situation.
Keywords: China; beast cancer; current treatment; questionnaire survey.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST The authors declare no potential conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The State of Surgical Axillary Management and Adjuvant Radiotherapy for Early-stage Invasive Breast Cancer in the Modern Era.Clin Breast Cancer. 2018 Aug;18(4):e477-e493. doi: 10.1016/j.clbc.2017.09.001. Epub 2017 Sep 19. Clin Breast Cancer. 2018. PMID: 29031423 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Axillary Dissection vs No Axillary Dissection on 10-Year Overall Survival Among Women With Invasive Breast Cancer and Sentinel Node Metastasis: The ACOSOG Z0011 (Alliance) Randomized Clinical Trial.JAMA. 2017 Sep 12;318(10):918-926. doi: 10.1001/jama.2017.11470. JAMA. 2017. PMID: 28898379 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Axillary management based on American college of surgeons oncology group Z0011 criteria makes it possible to omit intraoperative diagnosis of sentinel lymph nodes in early breast cancer patients.Breast J. 2021 Nov;27(11):804-810. doi: 10.1111/tbj.14291. Epub 2021 Sep 23. Breast J. 2021. PMID: 34558164
-
Evolution of axillary nodal staging in breast cancer: clinical implications of the ACOSOG Z0011 trial.Cancer Control. 2012 Oct;19(4):267-76. doi: 10.1177/107327481201900403. Cancer Control. 2012. PMID: 23037494 Review.
-
Axillary Management in Women with Early Breast Cancer and Limited Sentinel Node Metastasis: A Systematic Review and Metaanalysis of Real-World Evidence in the Post-ACOSOG Z0011 Era.Ann Surg Oncol. 2021 Feb;28(2):920-929. doi: 10.1245/s10434-020-08923-7. Epub 2020 Jul 23. Ann Surg Oncol. 2021. PMID: 32705512
Cited by
-
Spatial and temporal changes of breast-conserving surgery rates and its influential factors among Chinese patients with breast cancer from 2013 to 2019: a registry-based study.BMJ Open. 2025 Feb 2;15(1):e089188. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2024-089188. BMJ Open. 2025. PMID: 39894515 Free PMC article.
-
Application of the ACOSOG Z0011 criteria to Chinese patients with breast cancer: a prospective study.World J Surg Oncol. 2021 Apr 20;19(1):128. doi: 10.1186/s12957-021-02242-1. World J Surg Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33879180 Free PMC article.
-
Current Status and Factors Influencing Surgical Options for Breast Cancer in China: A Nationwide Cross-Sectional Survey of 110 Hospitals.Oncologist. 2020 Oct;25(10):e1473-e1480. doi: 10.1634/theoncologist.2020-0001. Epub 2020 May 13. Oncologist. 2020. PMID: 32333626 Free PMC article.
-
Predictive Factors for Unnecessary Axillary Dissection According to SLN Metastasis in T1, T2 Stage Breast Cancer.Indian J Surg Oncol. 2022 Dec;13(4):817-823. doi: 10.1007/s13193-022-01580-0. Epub 2022 Jul 2. Indian J Surg Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36687257 Free PMC article.
-
MRI-based artificial intelligence models for post-neoadjuvant surgery personalization in breast cancer: a narrative review of evidence from Western Pacific.Lancet Reg Health West Pac. 2024 Dec 6;57:101254. doi: 10.1016/j.lanwpc.2024.101254. eCollection 2025 Apr. Lancet Reg Health West Pac. 2024. PMID: 40443543 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J, Lortet-Tieulent J, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin. 2015;65:87–108. - PubMed
-
- Chen W, Zheng R, Baade PD, Zhang S, Zeng H, Bray F, Jemal A, Yu XQ, He J. Cancer statistics in China, 2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 2016;66:115–32. - PubMed
-
- Fan L, Zheng Y, Yu KD, Liu GY, Wu J, Lu JS, Shen KW, Shen ZZ, Shao ZM. Breast cancer in a transitional society over 18 years: trends and present status in Shanghai, China. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2009;117:409–16. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

